Diagnosing a faulty door control module involves checking power, ground, and communication signals, and DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN can equip you with the knowledge and tools for precise diagnostics. By understanding the LIN-Bus system and employing systematic testing, you can identify and resolve door module issues effectively. Learn about advanced diagnostic techniques, module testing, and wiring inspections to keep your vehicle in top condition, ensuring seamless operation of your vehicle’s door systems with comprehensive diagnostic procedures and cutting-edge car coding.
Contents
- 1. What is a Door Control Module and Its Function?
- 1.1 What Specific Functions Does a Door Control Module Manage?
- 1.2 How Does the Door Control Module Communicate with Other Vehicle Systems?
- 2. What are the Common Symptoms of a Failing Door Control Module?
- 2.1 What are the Key Indicators of a Faulty Door Control Module?
- 2.2 How Does a Failing DCM Affect the LIN-Bus System?
- 3. What Tools are Needed to Diagnose a Faulty Door Control Module?
- 3.1 What Essential Tools are Required for DCM Diagnostics?
- 3.2 How Does Ford’s IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System) Aid in Diagnostics?
- 4. What is the Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process for a Door Control Module?
- 4.1 What is the Initial Inspection and Basic Checks for DCM Issues?
- 4.2 How to Test the Power Supply to the Door Control Module?
- 4.3 How to Check the LIN-Bus Communication?
- 4.4 What Does a Jumper Wire Test Reveal About the LIN-Bus?
- 5. How to Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to Door Control Modules?
- 5.1 What are the Common DTCs Associated with Door Control Modules?
- 5.2 How to Use a Scan Tool to Retrieve and Understand DTCs?
- 6. What is the Role of Wiring Diagrams in Diagnosing Door Control Module Issues?
- 6.1 How do Wiring Diagrams Help in Tracing Electrical Circuits?
- 6.2 How to Identify Faults Using Wiring Diagrams?
- 7. What are the Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Door Control Modules?
- 7.1 How to Use an Oscilloscope to Analyze LIN-Bus Signals?
- 7.2 What are the Benefits of Using Advanced Scan Tools for DCM Diagnostics?
- 8. What are the Common Wiring Issues Affecting Door Control Modules?
- 8.1 What Types of Wiring Problems Can Occur in Door Systems?
- 8.2 How to Inspect and Repair Wiring Harnesses?
- 9. When Should You Consider Replacing the Door Control Module?
- 9.1 What Factors Indicate the Need for DCM Replacement?
- 9.2 How to Ensure Proper Installation and Programming of a New DCM?
- 10. What are the Best Practices for Maintaining Door Control Modules?
- 10.1 How Can Regular Maintenance Prevent DCM Failures?
- 10.2 What Environmental Factors Can Affect DCM Performance?
- 11. How Does Car Coding Relate to Diagnosing Door Control Module Faults?
- 11.1 What is Car Coding and its Importance in DCM Diagnostics?
- 11.2 What is the Role of DTS-Monaco Software in Car Coding for DCMs?
- 12. What Training and Resources are Available for Diagnosing Door Control Modules?
- 12.1 What Types of Training Programs are Available for Automotive Technicians?
- 12.2 Where Can You Find Reliable Resources for DCM Diagnostics and Car Coding?
- 13. How to Troubleshoot Door Control Module Issues in Different Vehicle Makes and Models?
- 13.1 What are the Key Differences in DCM Systems Across Different Vehicle Brands?
- 13.2 How to Adapt Your Diagnostic Approach for Specific Vehicle Models?
- 14. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Performing Car Coding on Door Control Modules?
- 14.1 What are the Potential Risks of Improper Car Coding?
- 14.2 How to Ensure Safe and Legal Car Coding Practices?
- 15. How to Stay Updated with the Latest Technologies in Door Control Module Diagnostics?
- 15.1 What Emerging Technologies are Impacting DCM Diagnostics?
- 15.2 How to Access and Utilize Resources for Continuous Learning?
- FAQ: Diagnosing a Faulty Door Control Module
- 1. How do I know if my door control module is faulty?
- 2. What tools do I need to diagnose a faulty door control module?
- 3. How do I test the power supply to the door control module?
- 4. How can I check the LIN-Bus communication?
- 5. What are some common DTCs associated with door control modules?
- 6. How do wiring diagrams help in diagnosing door control module issues?
- 7. When should I consider replacing the door control module?
- 8. How can regular maintenance prevent DCM failures?
- 9. What is the role of car coding in diagnosing door control module faults?
- 10. What resources are available for learning about door control module diagnostics and car coding?
1. What is a Door Control Module and Its Function?
A door control module (DCM) is an electronic control unit (ECU) that manages various functions within a vehicle’s door, ensuring smooth operation of door-related systems. These functions include power windows, door locks, side mirrors, and even puddle lamps, centralizing control and enhancing convenience. The DCM receives commands from switches operated by the user, such as window and lock controls, and translates these commands into actions, such as activating the window motor or locking the door. The door control module (DCM) is essential for managing a vehicle’s door functions efficiently.
1.1 What Specific Functions Does a Door Control Module Manage?
A door control module handles several key functions, including:
- Power Windows: Controls the raising and lowering of windows.
- Door Locks: Manages the locking and unlocking of doors.
- Side Mirrors: Adjusts mirror positions and activates heating functions.
- Puddle Lamps: Illuminates the area around the door for enhanced visibility.
1.2 How Does the Door Control Module Communicate with Other Vehicle Systems?
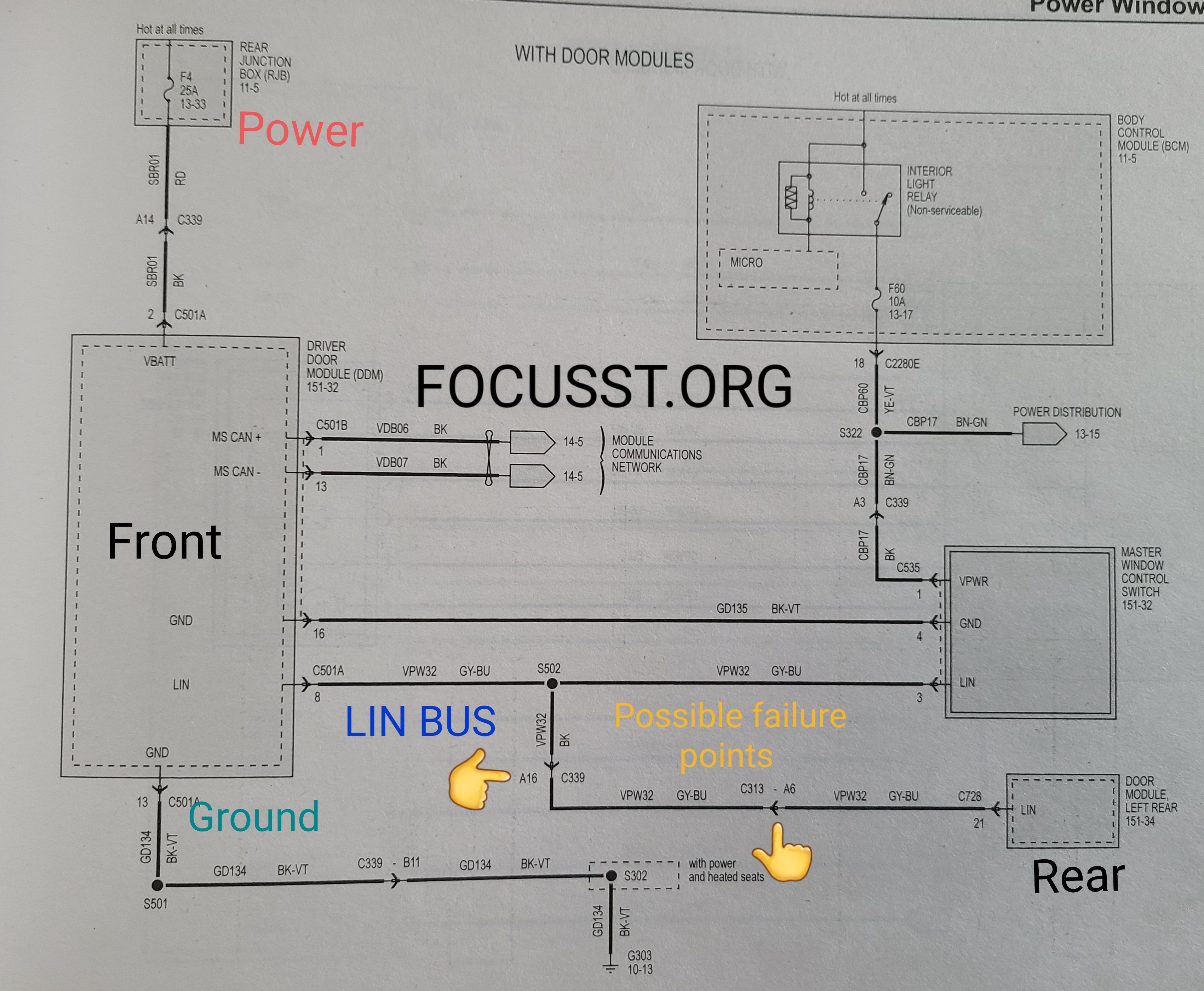
The DCM communicates with other vehicle systems through a Local Interconnect Network (LIN-Bus). This network allows the DCM to receive instructions from the Body Control Module (BCM) and transmit signals to other modules, facilitating coordinated actions across the vehicle. The LIN-Bus reduces the amount of physical wiring required, simplifying the vehicle’s electrical system while adding a layer of complexity that requires specialized tools for effective troubleshooting.
2. What are the Common Symptoms of a Failing Door Control Module?
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing door control module is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair, maintaining optimal vehicle performance. Several key indicators can signal that a door control module is malfunctioning, ensuring you can address the issue before it escalates.
2.1 What are the Key Indicators of a Faulty Door Control Module?
Common symptoms include:
- Non-functional Power Windows: Windows that fail to respond to switch commands.
- Door Locks Not Working: Inability to lock or unlock doors using the power locks.
- Malfunctioning Side Mirrors: Mirrors that cannot be adjusted or heated.
- Inoperative Puddle Lamps: Puddle lamps that do not illuminate when the door is opened.
- Switch Illumination Issues: Door switch lights that do not illuminate.
- Master Switch Failure: The driver’s side master switch failing to control door functions.
2.2 How Does a Failing DCM Affect the LIN-Bus System?
A failing DCM can disrupt the LIN-Bus system, leading to communication issues between modules. This can manifest as intermittent or complete failure of door functions, making it difficult for the BCM to coordinate actions. A damaged or malfunctioning LIN-Bus can prevent the rear module from functioning, impacting overall vehicle performance.
3. What Tools are Needed to Diagnose a Faulty Door Control Module?
To effectively diagnose a faulty door control module, you will need a range of diagnostic tools. Having the right tools ensures you can accurately identify and address the problem, restoring your vehicle’s functionality.
3.1 What Essential Tools are Required for DCM Diagnostics?
Essential tools include:
- Multimeter: For testing voltage, continuity, and resistance.
- Scan Tool: Capable of reading B-series codes to diagnose module issues.
- Oscilloscope: For analyzing the LIN-Bus signal.
- Jumper Wires: To bypass potentially damaged wiring.
- Wiring Diagrams: To understand the circuit layout.
3.2 How Does Ford’s IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System) Aid in Diagnostics?
Ford’s IDS is a specialized software and scanner that communicates with vehicle modules to test their status and communication capabilities. This tool allows technicians to access detailed diagnostic information, making it easier to pinpoint issues within the door control module and related systems. According to Ford Motor Company, the IDS tool provides comprehensive diagnostics, programming, and module configuration for Ford vehicles, ensuring accurate and efficient troubleshooting.
4. What is the Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process for a Door Control Module?
Diagnosing a door control module requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem. Following a step-by-step process ensures thoroughness and accuracy, leading to effective repairs.
4.1 What is the Initial Inspection and Basic Checks for DCM Issues?
Begin with basic checks, including:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage to the door module and wiring.
- Fuse Check: Verify the fuse for the door module is intact and functioning correctly. Use a multimeter to test both sides of the fuse for battery voltage.
- Power and Ground Verification: Ensure the module is receiving proper power and ground.
4.2 How to Test the Power Supply to the Door Control Module?
To test the power supply:
- Locate the DCM Connector: Remove the inner door shell to access the door module’s connector.
- Voltage Test: Set the multimeter to DC volts and place the red lead into the power pin and the black lead into the ground pin.
- Compare Readings: Verify the voltage reading matches the supply voltage from the fuse.
4.3 How to Check the LIN-Bus Communication?
Checking LIN-Bus communication involves:
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter set to ohms to test the continuity between the front and rear door modules.
- Resistance Measurement: Measure the resistance on the LIN wire. A reading close to zero ohms indicates good continuity.
- Jumper Wire Test: Bypass the LIN wire with a jumper wire to test if communication is restored.
4.4 What Does a Jumper Wire Test Reveal About the LIN-Bus?
A jumper wire test helps determine if the issue lies within the LIN-Bus wiring. By bypassing the original wire, you can assess whether a damaged wire is preventing proper communication between the modules. If the system functions correctly with the jumper wire, the original wiring is likely the source of the problem.
5. How to Interpret Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to Door Control Modules?
Interpreting Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is essential for accurately diagnosing issues with door control modules. DTCs provide specific information about the nature and location of the problem, streamlining the repair process.
5.1 What are the Common DTCs Associated with Door Control Modules?
Common DTCs include codes related to:
- Power Supply Issues: Indicating problems with voltage or ground.
- LIN-Bus Communication Errors: Highlighting disruptions in communication between modules.
- Actuator Faults: Identifying issues with door lock or window motor functionality.
- Internal Module Failures: Suggesting the DCM itself is malfunctioning.
5.2 How to Use a Scan Tool to Retrieve and Understand DTCs?
To use a scan tool effectively:
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the scan tool into the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Retrieve Codes: Follow the scan tool’s instructions to read and display the DTCs.
- Interpret Codes: Use a repair manual or online database to understand the meaning of each code and its potential causes.
- Clear Codes: After addressing the issues, clear the DTCs and retest the system to ensure the problem is resolved.
6. What is the Role of Wiring Diagrams in Diagnosing Door Control Module Issues?
Wiring diagrams are invaluable tools for diagnosing door control module issues, providing a clear roadmap of the electrical circuits involved. These diagrams help technicians trace circuits, identify potential faults, and perform accurate tests, saving time and improving the precision of repairs.
6.1 How do Wiring Diagrams Help in Tracing Electrical Circuits?
Wiring diagrams illustrate the layout of electrical circuits, showing the connections between various components. By following the lines and symbols on the diagram, you can trace the path of electricity and identify potential breaks or shorts in the circuit.
6.2 How to Identify Faults Using Wiring Diagrams?
Using wiring diagrams, you can:
- Locate Components: Find the exact location of the door control module, fuses, and connectors.
- Trace Wires: Follow specific wires to check for continuity and shorts.
- Identify Ground Points: Ensure proper grounding for the module and related components.
- Verify Connections: Confirm that all connections are secure and properly connected.
7. What are the Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Door Control Modules?
Advanced diagnostic techniques offer deeper insights into the functioning of door control modules, enabling precise and effective troubleshooting. These methods require specialized tools and expertise but can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy.
7.1 How to Use an Oscilloscope to Analyze LIN-Bus Signals?
An oscilloscope allows you to visualize the LIN-Bus signal, providing detailed information about its integrity. By connecting the oscilloscope to the LIN wire, you can:
- Measure Signal Voltage: Verify that the signal voltage is within the specified range.
- Check Signal Shape: Identify any distortions or anomalies in the signal waveform.
- Detect Communication Errors: Look for missing or corrupted data packets.
7.2 What are the Benefits of Using Advanced Scan Tools for DCM Diagnostics?
Advanced scan tools, like Ford’s IDS, offer several benefits:
- Module Programming: Allows you to reprogram or update the door control module’s software.
- Parameter Reset: Resets learned parameters to default values.
- Bi-Directional Control: Enables you to send commands to the module to test its functions.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Provides live data from the module, helping you identify intermittent issues.
8. What are the Common Wiring Issues Affecting Door Control Modules?
Wiring issues are a frequent cause of door control module problems. Identifying and addressing these issues is crucial for restoring proper functionality and preventing future failures.
8.1 What Types of Wiring Problems Can Occur in Door Systems?
Common wiring problems include:
- Broken Wires: Caused by wear and tear, especially in areas that flex with door movement.
- Corroded Connectors: Resulting from moisture and environmental exposure.
- Short Circuits: Due to damaged insulation or improper wiring.
- Loose Connections: Leading to intermittent failures.
8.2 How to Inspect and Repair Wiring Harnesses?
To inspect and repair wiring harnesses:
- Visual Inspection: Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or corroded connectors.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of each wire.
- Connector Cleaning: Clean corroded connectors with a wire brush or contact cleaner.
- Wire Repair: Repair broken wires by soldering and insulating the connection.
- Harness Replacement: Replace entire wiring harnesses if damage is extensive.
 Testing Continuity on a Car Door Module Connector
Testing Continuity on a Car Door Module Connector
9. When Should You Consider Replacing the Door Control Module?
Knowing when to replace the door control module is crucial for avoiding unnecessary repairs and ensuring the vehicle’s systems function correctly. Several factors can indicate that replacement is the best course of action.
9.1 What Factors Indicate the Need for DCM Replacement?
Consider replacing the DCM if:
- Internal Failure: The module shows signs of internal damage or malfunction.
- Non-Responsive Module: The module does not respond to diagnostic commands.
- Irreparable Wiring Damage: The wiring harness is severely damaged and cannot be repaired.
- Persistent DTCs: DTCs related to the DCM remain after troubleshooting and repairs.
9.2 How to Ensure Proper Installation and Programming of a New DCM?
To ensure proper installation and programming:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the vehicle’s battery before replacing the module.
- Install the New Module: Connect the new DCM and secure it in place.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Program the Module: Use a scan tool to program the new module with the correct software and parameters.
- Verify Functionality: Test all door functions to ensure the new module is working correctly.
10. What are the Best Practices for Maintaining Door Control Modules?
Maintaining door control modules involves proactive measures to prevent failures and ensure long-term reliability. Following best practices can extend the life of the DCM and maintain optimal vehicle performance.
10.1 How Can Regular Maintenance Prevent DCM Failures?
Regular maintenance includes:
- Inspecting Wiring: Periodically check wiring harnesses for damage and corrosion.
- Cleaning Connectors: Keep connectors clean and free of moisture.
- Ensuring Proper Grounding: Verify that the module and related components are properly grounded.
- Updating Software: Keep the DCM software up to date with the latest versions.
10.2 What Environmental Factors Can Affect DCM Performance?
Environmental factors that can affect DCM performance include:
- Moisture: Can cause corrosion and short circuits.
- Extreme Temperatures: Can damage electronic components.
- Vibration: Can loosen connections and cause wiring to fail.
- Dust and Debris: Can accumulate in connectors and cause malfunctions.
11. How Does Car Coding Relate to Diagnosing Door Control Module Faults?
Car coding is essential in diagnosing and resolving door control module faults, enabling technicians to reprogram or update module settings. This process ensures that the DCM functions correctly with other vehicle systems and adheres to the vehicle’s specifications.
11.1 What is Car Coding and its Importance in DCM Diagnostics?
Car coding involves modifying the software settings of a vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs), including door control modules. It is crucial for:
- Configuration: Setting up the DCM to match the vehicle’s specific options and features.
- Calibration: Adjusting parameters to optimize performance and reliability.
- Software Updates: Installing the latest software versions to fix bugs and improve functionality.
- Module Replacement: Ensuring a new DCM works seamlessly with the vehicle’s existing systems.
11.2 What is the Role of DTS-Monaco Software in Car Coding for DCMs?
DTS-Monaco software is a powerful tool used for car coding, diagnostics, and engineering tasks on Mercedes-Benz vehicles and other brands. Its role in DCM diagnostics includes:
- Advanced Diagnostics: Performing in-depth analysis of the DCM’s performance and identifying faults.
- Module Programming: Reprogramming the DCM with the correct software and settings.
- Parameter Adjustment: Modifying parameters to fine-tune the DCM’s operation.
- Data Logging: Recording data from the DCM to analyze its behavior under different conditions.
According to Mercedes-Benz, DTS-Monaco is a primary tool for ECU diagnostics and programming, providing comprehensive capabilities for automotive technicians and engineers.
12. What Training and Resources are Available for Diagnosing Door Control Modules?
Proper training and access to reliable resources are essential for effectively diagnosing door control modules. These resources help technicians stay updated with the latest diagnostic techniques and tools, ensuring accurate and efficient repairs.
12.1 What Types of Training Programs are Available for Automotive Technicians?
Various training programs are available, including:
- Vocational Schools: Offering comprehensive automotive technology courses.
- Online Courses: Providing flexible learning options for specific diagnostic and repair techniques.
- Manufacturer-Specific Training: Offered by vehicle manufacturers like Ford and Mercedes-Benz.
- Professional Certifications: Such as those offered by ASE (Automotive Service Excellence).
12.2 Where Can You Find Reliable Resources for DCM Diagnostics and Car Coding?
Reliable resources include:
- DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN: Offers training, software, and support for car coding and diagnostics.
Address: 275 N Harrison St, Chandler, AZ 85225, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. - Automotive Repair Manuals: Providing detailed information on diagnostic procedures and wiring diagrams.
- Online Forums and Communities: Where technicians share their knowledge and experiences.
- Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs): Issued by vehicle manufacturers to address common issues.
13. How to Troubleshoot Door Control Module Issues in Different Vehicle Makes and Models?
Troubleshooting door control module issues can vary depending on the vehicle make and model. Understanding these differences and tailoring your diagnostic approach accordingly is essential for effective repairs.
13.1 What are the Key Differences in DCM Systems Across Different Vehicle Brands?
Key differences include:
- Wiring Layouts: Different brands may use different wiring configurations and connector types.
- Communication Protocols: Some vehicles use different communication protocols for the LIN-Bus.
- Module Programming: Programming procedures can vary significantly between brands.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: DTC definitions may differ across different makes and models.
13.2 How to Adapt Your Diagnostic Approach for Specific Vehicle Models?
To adapt your diagnostic approach:
- Consult Vehicle-Specific Resources: Use repair manuals and wiring diagrams specific to the vehicle model.
- Research Common Issues: Look for known problems and solutions for the specific make and model.
- Use the Correct Scan Tool: Ensure your scan tool is compatible with the vehicle’s diagnostic system.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended procedures for diagnostics and repairs.
14. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Performing Car Coding on Door Control Modules?
Performing car coding on door control modules involves ethical considerations that technicians need to be aware of. These considerations ensure that coding practices are safe, legal, and do not compromise vehicle integrity.
14.1 What are the Potential Risks of Improper Car Coding?
Improper car coding can lead to:
- System Malfunctions: Incorrect settings can cause the DCM and other systems to malfunction.
- Safety Issues: Faulty coding can compromise safety features like door locks and windows.
- Warranty Voidance: Unauthorized coding can void the vehicle’s warranty.
- Legal Liabilities: Illegal modifications can result in legal consequences.
14.2 How to Ensure Safe and Legal Car Coding Practices?
To ensure safe and legal practices:
- Use Reliable Software: Only use trusted and verified car coding software like DTS-Monaco.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended procedures.
- Backup Original Settings: Always back up the original module settings before making changes.
- Verify Compatibility: Ensure that any modifications are compatible with the vehicle’s systems.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest car coding techniques and regulations.
15. How to Stay Updated with the Latest Technologies in Door Control Module Diagnostics?
Staying updated with the latest technologies in door control module diagnostics is essential for automotive technicians to remain competitive and provide the best possible service. Continuous learning and adaptation are key in this rapidly evolving field.
15.1 What Emerging Technologies are Impacting DCM Diagnostics?
Emerging technologies include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze data and identify faults more quickly and accurately.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Cloud platforms provide access to vast databases of diagnostic information and remote support.
- Wireless Diagnostics: Wireless scan tools and sensors allow for more convenient and flexible diagnostics.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR applications can overlay diagnostic information onto the vehicle, providing step-by-step guidance.
15.2 How to Access and Utilize Resources for Continuous Learning?
To access and utilize resources:
- Attend Industry Conferences: Participate in automotive industry conferences and trade shows.
- Join Professional Organizations: Become a member of organizations like ASE to access training and resources.
- Subscribe to Industry Publications: Read automotive magazines and online publications.
- Engage in Online Communities: Participate in online forums and communities to share knowledge and learn from others.
- Take Advanced Training Courses: Enroll in advanced training courses offered by manufacturers and training providers.
Mastering door control module diagnostics requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and the right tools. By following a systematic approach, understanding wiring diagrams, and utilizing advanced diagnostic techniques, you can effectively troubleshoot and repair DCM issues. Stay updated with the latest technologies and resources to ensure you are always providing the best possible service. If you’re looking to enhance your skills and knowledge, consider exploring the training programs and resources offered by DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN. With the right education and tools, you can confidently tackle any door control module challenge.
FAQ: Diagnosing a Faulty Door Control Module
1. How do I know if my door control module is faulty?
Key symptoms include non-functional power windows, door locks not working, malfunctioning side mirrors, inoperative puddle lamps, switch illumination issues, and failure of the master switch.
2. What tools do I need to diagnose a faulty door control module?
You’ll need a multimeter, scan tool, oscilloscope, jumper wires, and wiring diagrams.
3. How do I test the power supply to the door control module?
Remove the inner door shell, access the DCM connector, and use a multimeter to verify the voltage reading matches the supply voltage from the fuse.
4. How can I check the LIN-Bus communication?
Use a multimeter to perform a continuity test between the front and rear door modules, measure the resistance on the LIN wire, and bypass the LIN wire with a jumper wire to see if communication is restored.
5. What are some common DTCs associated with door control modules?
Common DTCs include codes related to power supply issues, LIN-Bus communication errors, actuator faults, and internal module failures.
6. How do wiring diagrams help in diagnosing door control module issues?
Wiring diagrams help in tracing electrical circuits, locating components, and identifying faults such as broken wires, corroded connectors, and short circuits.
7. When should I consider replacing the door control module?
Consider replacing the DCM if there is internal failure, a non-responsive module, irreparable wiring damage, or persistent DTCs.
8. How can regular maintenance prevent DCM failures?
Regular maintenance includes inspecting wiring, cleaning connectors, ensuring proper grounding, and updating software.
9. What is the role of car coding in diagnosing door control module faults?
Car coding involves reprogramming or updating module settings to ensure the DCM functions correctly with other vehicle systems.
10. What resources are available for learning about door control module diagnostics and car coding?
Resources include vocational schools, online courses, manufacturer-specific training, automotive repair manuals, online forums, and technical service bulletins. Check out DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN for specialized training and resources. Address: 275 N Harrison St, Chandler, AZ 85225, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880.
Ready to elevate your car coding and diagnostic skills? Visit DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive training programs, cutting-edge software, and expert support. Don’t let faulty door control modules slow you down – unlock the full potential of your automotive expertise now!
