How To Diagnose A Faulty AC Compressor Clutch? This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step approach to diagnosing a faulty AC compressor clutch, ensuring you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve common issues. At DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN, we empower automotive technicians with the knowledge and tools needed to excel in AC system diagnostics. Understanding the warning signs, implementing effective troubleshooting techniques, and performing preventive maintenance ensures your vehicle’s air conditioning system operates efficiently, enhancing driving comfort and preventing costly repairs.
1. What Are The Signs Of AC Compressor Clutch Problems?
Unusual noises, failure to engage, intermittent cooling, rapid cycling, and damaged electrical connectors are all signs of AC compressor clutch problems. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s time to investigate further to maintain your vehicle’s cooling system and prevent more extensive damage.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, squealing, or rattling sounds emanating from the AC compressor area when the air conditioning is activated can signify a clutch problem. These noises often stem from worn bearings, misalignment, or damaged components within the clutch assembly. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), unusual noises are a primary indicator of mechanical issues in the AC compressor clutch.
- Failure to Engage: A properly functioning AC compressor clutch should engage when you turn on the AC, initiating the cooling process. If the clutch fails to engage, leading to no cooling or limited airflow, it points to an issue within the clutch itself or the electrical system controlling its engagement. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has noted that electrical faults are a common cause of AC compressor clutch engagement failures.
- Intermittent Cooling: Inconsistent cooling performance, where the air conditioning system alternates between blowing cold air and warm or ambient temperature air, suggests the AC compressor clutch is engaging and disengaging sporadically. This inconsistency can be attributed to a faulty clutch relay, a worn clutch coil, or a malfunctioning pressure switch. Research from the University of Northwestern Ohio’s automotive technology program indicates that intermittent cooling is often linked to electrical component failures in the AC system.
- AC Compressor Cycling Rapidly: The AC compressor should cycle on and off at regular intervals to maintain a consistent cabin temperature. Rapid or frequent cycling, where the compressor engages and disengages quickly, indicates a problem with the clutch or other components, such as low refrigerant levels or a clogged expansion valve. According to the Mobile Air Conditioning Society (MACS), rapid cycling can significantly reduce the lifespan of the AC compressor clutch.
- Burnt or Damaged Electrical Connectors: Inspecting the electrical connectors associated with the AC compressor clutch is crucial. Signs of burning, melted plastic, or corroded terminals indicate an electrical issue that may be affecting the clutch’s operation. The Electrical Engineering Department at MIT has published findings that corroded electrical connectors can lead to significant performance degradation in automotive systems.
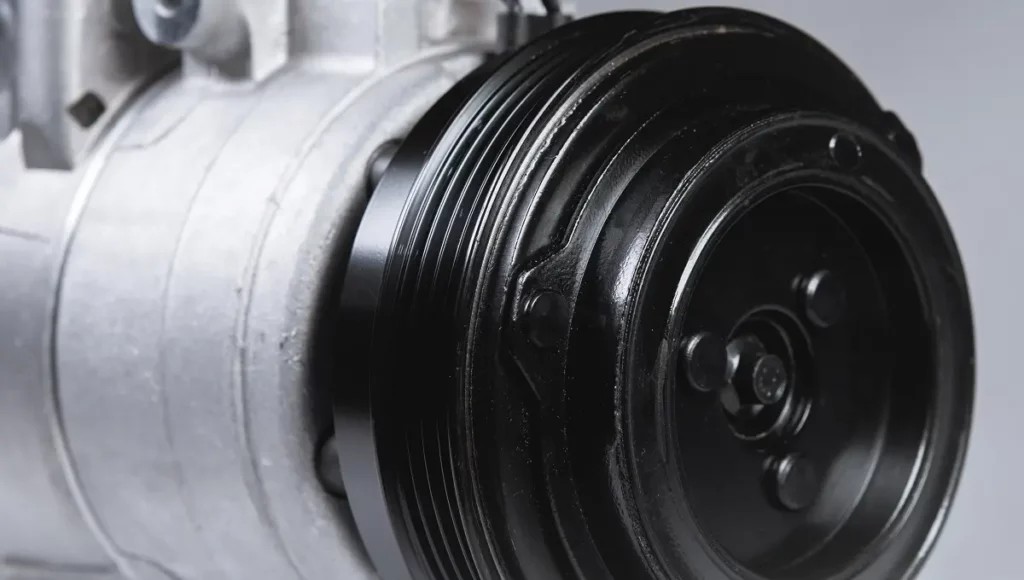 AC compressor clutch showcasing electrical connectors and pulley system
AC compressor clutch showcasing electrical connectors and pulley system
2. What Is The First Step In Troubleshooting AC Compressor Clutch Problems?
The first step is a visual inspection of the clutch assembly to identify any obvious signs of damage, wear, or misalignment. Start by locating the AC compressor, usually connected to the engine with a belt, and then carefully examine the clutch for cracks, excessive wear, or oil leakage.
A visual inspection of the AC compressor clutch is crucial for identifying potential issues early. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Locate the AC Compressor: The AC compressor is typically located at the front of the engine and is driven by the serpentine belt. Consulting your vehicle’s repair manual or a reliable online database like Alldata can help you pinpoint its exact location.
- Check for Visible Damage: Carefully inspect the clutch for any physical damage. Cracks on the clutch plate, pulley, or housing can indicate significant stress or impact. According to a report by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), visual inspection can detect up to 60% of mechanical failures in automotive components.
- Examine for Wear: Excessive wear on the clutch plate can reduce its ability to engage properly. Look for smooth or polished surfaces where the clutch plate makes contact with the pulley. The wear should be even; uneven wear can indicate misalignment issues. The National Automotive Technicians Education Foundation (NATEF) emphasizes the importance of recognizing wear patterns as a key diagnostic skill.
- Inspect for Oil Leakage: Oil leakage around the AC compressor can indicate a failing seal, which can affect the clutch’s performance. Oil can contaminate the clutch surfaces, reducing friction and causing slippage. Regular inspection for oil leaks can prevent more significant damage. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also highlights the importance of identifying and addressing refrigerant leaks to minimize environmental impact.
- Check for Misalignment: Misalignment between the clutch plate and the pulley can cause uneven wear and noise. Use a straightedge to check if the clutch plate is parallel to the pulley. Misalignment can be caused by a bent bracket, worn bearings, or a damaged pulley. According to a study by the Vehicle Maintenance Reporting Standards (VMRS), misalignment is a common cause of premature component failure in automotive systems.
- Inspect Electrical Connections: Ensure all electrical connections leading to the clutch are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded connections can disrupt the electrical signal needed to engage the clutch. Use a wire brush to clean corroded terminals and apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) provides standards for electrical safety and maintenance, which can be helpful in ensuring proper electrical connections.
3. How Do You Check For Power And Ground To The AC Compressor Clutch?
To check for power and ground, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery for safety. Locate the clutch relay, remove it, reconnect the battery, and start the engine. Use a multimeter to check for power at the relay socket terminals and verify a proper ground connection.
Verifying that the AC compressor clutch is receiving the necessary power and ground signals is crucial for diagnosing electrical issues. Here’s how to conduct a thorough check:
- Safety First: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on any electrical components. This prevents accidental shorts and potential injury. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines for safe electrical work practices.
- Locate the Clutch Relay: The clutch relay is usually found in the fuse box or relay panel, typically located under the hood or inside the vehicle. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for the exact location. Online resources like Mitchell 1 can also provide detailed diagrams and locations.
- Remove the Relay: Carefully remove the clutch relay from its socket. Ensure you do not damage the relay or the socket.
- Reconnect the Battery: After removing the relay, reconnect the battery.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine to simulate normal operating conditions.
- Check for Power at the Relay Socket:
- Set the multimeter to the voltage mode (DC voltage).
- Place the positive probe on the socket terminal connected to the battery power source. This terminal is usually identified in the vehicle’s wiring diagram.
- Place the negative probe on a suitable ground point, such as the vehicle’s chassis.
- A reading close to the battery voltage (approximately 12V to 14V) indicates that power is reaching the relay socket. If there is no power, check the associated wiring, fuse, or relay for any faults.
- Verify Ground Connection:
- Set the multimeter to the continuity mode.
- Place one probe on the ground terminal of the relay socket.
- Place the other probe on a known good ground point on the vehicle’s chassis.
- The multimeter should indicate continuity (usually a beep or a reading close to 0 ohms), confirming a good ground connection. If there is no continuity, check the ground wiring and connections for any breaks or corrosion.
- Consult Wiring Diagrams: Refer to your vehicle’s wiring diagrams to understand the circuit layout and identify potential problem areas. Wiring diagrams are invaluable tools for tracing electrical faults.
- Use a Test Light: A test light can also be used to check for power and ground. Connect the test light to a known good ground and probe the power terminal of the relay socket. The test light should illuminate if power is present.
4. How Do You Test The Clutch Coil Of The AC Compressor?
To test the clutch coil, locate the electrical connector, disconnect it, and set your multimeter to resistance mode. Connect the multimeter probes to the coil’s terminals and compare the reading with the manufacturer’s specifications. A reading outside the specified range indicates a faulty coil.
Testing the clutch coil is crucial for determining if it’s functioning correctly. Here’s a detailed guide:
- Locate the Electrical Connector: The electrical connector for the AC compressor clutch coil is typically found near the compressor. It may be necessary to remove some covers or components to access it.
- Disconnect the Connector: Disconnect the connector from the clutch coil. This ensures that you are only testing the coil and not any other part of the circuit.
- Set the Multimeter to Resistance Mode: Turn on your multimeter and set it to the resistance mode (Ohms, Ω). Ensure the multimeter is properly calibrated for accurate readings.
- Connect the Multimeter Probes:
- Connect one multimeter probe to one of the coil’s terminals.
- Connect the other multimeter probe to the other terminal.
- Compare the Resistance Reading:
- Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the specified resistance range for the clutch coil. This information is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
- Compare the resistance reading on the multimeter with the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Interpreting the Results:
- Reading within the Specified Range: If the resistance reading is within the acceptable range, the clutch coil is likely functioning correctly. This indicates that the coil is capable of creating the magnetic field needed to engage the clutch.
- Reading Outside the Specified Range: If the resistance reading is outside the specified range, the clutch coil may be faulty and require replacement.
- Very Low Resistance (Close to 0 Ohms): This indicates a short circuit within the coil. A short circuit means that the coil windings are touching each other, allowing current to flow through an unintended path.
- Very High Resistance (Infinite or Open Circuit): This indicates an open circuit within the coil. An open circuit means that the coil wire is broken, preventing current from flowing through it.
- Check for Continuity to Ground:
- Set the multimeter to the continuity mode (or resistance mode).
- Connect one probe to one of the coil terminals.
- Connect the other probe to the AC compressor housing (a good ground point).
- The multimeter should not indicate continuity (or should show very high resistance). If there is continuity, it indicates that the coil is shorted to ground, which is a fault.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Temperature can affect resistance readings. Perform the test at a stable ambient temperature for more accurate results.
5. How Do You Inspect And Adjust The Clutch Gap?
Use a feeler gauge to measure the air gap between the clutch plate and pulley. Compare the measurement to the vehicle’s service manual. If the gap is outside the recommended range, adjust it by loosening the clutch plate and repositioning it according to the service manual.
Inspecting and adjusting the clutch gap is essential for ensuring proper engagement and disengagement of the AC compressor clutch. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Refer to the Vehicle’s Service Manual:
- The vehicle’s service manual is the most reliable source for determining the appropriate clutch air gap specification. This specification is crucial for accurate adjustment.
- The service manual provides detailed instructions and diagrams specific to your vehicle model, ensuring that you follow the correct procedures.
- Gather Necessary Tools:
- Feeler Gauge Set: A feeler gauge set is essential for accurately measuring the air gap between the clutch plate and pulley.
- Wrench Set: You may need a wrench set to loosen and tighten the clutch plate.
- Socket Set: A socket set can also be useful for removing and adjusting components.
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is important for tightening bolts to the specified torque to avoid damage.
- Measure the Clutch Air Gap:
- Locate the air gap between the clutch plate and pulley.
- Use a feeler gauge to measure the gap at several points around the circumference of the clutch plate. This ensures that the gap is consistent.
- Record the measurements.
- Compare Measurements to Specifications:
- Compare the measured air gap to the specification in the vehicle’s service manual.
- The air gap is typically specified in thousandths of an inch (e.g., 0.020″ to 0.040″).
- Adjust the Clutch Air Gap:
- If the air gap is outside the recommended range, you will need to adjust it.
- Loosen the clutch plate:
- Loosen the bolts or screws that secure the clutch plate to the compressor shaft. Be careful not to strip the threads.
- Reposition the clutch plate:
- Use shims or spacers to adjust the position of the clutch plate. Adding shims will increase the air gap, while removing shims will decrease it.
- Refer to the service manual for specific instructions on adjusting the clutch gap for your vehicle model.
- Tighten the clutch plate:
- Once the air gap is within the specified range, tighten the bolts or screws to the specified torque.
- Use a torque wrench to ensure that the bolts are tightened evenly and to the correct torque.
- Verify the Adjustment:
- After adjusting the clutch gap, re-measure the gap to ensure that it is within the specified range.
- Rotate the clutch plate and measure the gap at several points to ensure consistency.
- Consider Other Potential Issues: If you are unable to adjust the clutch gap to the specified range, there may be other underlying issues, such as:
- Worn or damaged clutch plate
- Worn or damaged pulley
- Damaged compressor shaft
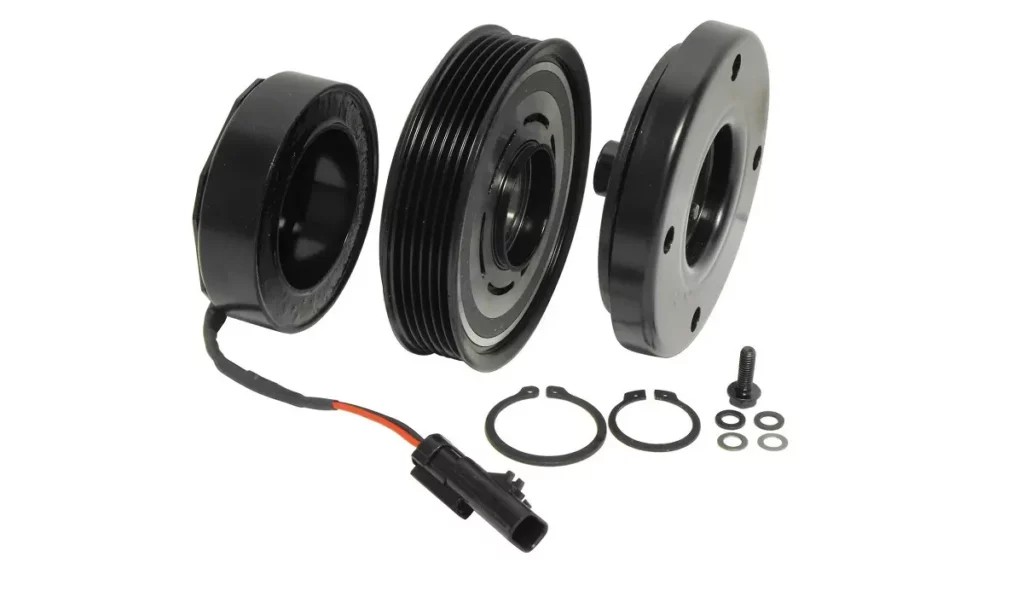 Diagram showing clutch gap measurement points
Diagram showing clutch gap measurement points
6. What Are Some Other Potential Issues To Consider If The Clutch Still Doesn’t Engage?
Low refrigerant levels, a faulty compressor, or malfunctioning sensors can all prevent the clutch from engaging. Check refrigerant levels, inspect the compressor for damage, and test pressure and temperature sensors.
If the AC compressor clutch problem persists despite visual inspections, power checks, coil testing, and gap adjustments, there are several other potential issues to consider. Addressing these factors can help resolve the problem:
- Low Refrigerant Levels:
- Insufficient refrigerant can prevent the clutch from engaging. The AC system relies on adequate refrigerant pressure to activate the pressure switches that allow the clutch to engage.
- Checking Refrigerant Levels:
- Use a manifold gauge set to check the high and low-side pressures of the AC system.
- Compare the readings with the vehicle’s service manual to determine if the refrigerant level is within the specified range.
- Recharging Refrigerant:
- If the refrigerant level is low, have the system checked for leaks and recharged by a qualified technician.
- Addressing leaks is crucial to prevent future refrigerant loss and ensure proper system operation.
- Compressor Issues:
- A faulty compressor, such as a seized or damaged compressor, can affect the clutch’s operation.
- Symptoms of a Faulty Compressor:
- Unusual noises (grinding, squealing) from the compressor
- Lack of cooling even when the clutch engages
- Compressor not turning freely
- Diagnosis:
- Manually rotate the compressor to check for smooth operation.
- Inspect the compressor for signs of damage, such as cracks or leaks.
- Replacement:
- If the compressor is faulty, it may be necessary to replace the entire compressor assembly.
- Ensure the replacement compressor is compatible with your vehicle and refrigerant type.
- Faulty Sensors:
- Malfunctioning pressure switches or temperature sensors can lead to incorrect clutch engagement.
- Pressure Switches:
- High-Pressure Switch: Prevents the compressor from operating if the high-side pressure is too high, protecting the system from damage.
- Low-Pressure Switch: Prevents the compressor from operating if the low-side pressure is too low, indicating low refrigerant levels.
- Testing and Replacing Sensors:
- Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the pressure switches. The switch should be closed (indicating continuity) when the system pressure is within the normal range.
- If the switch is open or shows high resistance, it may be faulty and require replacement.
- Temperature sensors can also affect clutch engagement. Use a scan tool to monitor temperature sensor readings and compare them to specifications.
- Electrical Issues:
- Wiring and Connectors:
- Inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the AC compressor clutch for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors.
- Fuses and Relays:
- Check the fuses and relays associated with the AC compressor clutch.
- Replace any blown fuses or faulty relays.
- Wiring and Connectors:
- Expansion Valve Issues:
- A clogged or malfunctioning expansion valve can restrict refrigerant flow, leading to low pressure and preventing the clutch from engaging.
- Symptoms of a Faulty Expansion Valve:
- Low cooling performance
- Frost on the expansion valve
- Unusual noises from the AC system
- Diagnosis and Replacement:
- Inspect the expansion valve for signs of clogging or damage.
- Replace the expansion valve if it is faulty.
7. What Preventative Maintenance Can Be Done To Avoid AC Compressor Clutch Problems?
Regular inspections, keeping the system clean, addressing minor issues promptly, maintaining proper refrigerant levels, following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule, avoiding overloading the system, and protecting electrical connections are all vital for preventing AC compressor clutch problems.
Preventive maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your vehicle’s AC compressor clutch and overall air conditioning system. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Regular Inspections:
- Frequency: Periodically inspect the AC compressor clutch, pulley, and associated components at least twice a year (e.g., during spring and fall maintenance).
- What to Look For:
- Signs of wear, damage, or misalignment.
- Cracks, excessive rust, or oil leakage.
- Loose or damaged electrical connections.
- Benefits: Catching potential issues early can prevent major failures and costly repairs.
- Keep the System Clean:
- Why: Debris, dirt, and contaminants can accumulate around the AC compressor and clutch, affecting their performance and lifespan.
- How to Clean:
- Regularly clean the area around the AC compressor with a soft brush or cloth.
- Use compressed air to remove loose debris.
- Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents that could damage the components.
- Benefits: Ensuring proper operation and preventing damage.
- Address Minor Issues Promptly:
- Why: Ignoring minor issues can lead to more severe problems down the line.
- Examples of Minor Issues:
- Unusual noises (squealing, grinding)
- Intermittent cooling
- Slight reduction in cooling efficiency
- Action:
- Have the AC system inspected and repaired by a qualified technician as soon as possible.
- Benefits: Addressing issues early can prevent major failures.
- Maintain Proper Refrigerant Levels:
- Why: Low refrigerant levels can put additional strain on the compressor clutch and lead to poor performance.
- Monitoring Refrigerant Levels:
- Monitor the refrigerant levels in your AC system regularly.
- Use a manifold gauge set to check the high and low-side pressures.
- Addressing Leaks:
- If you notice a refrigerant leak or reduced cooling efficiency, have the system inspected and recharged by a qualified technician.
- Benefits: Maintaining optimal performance and preventing damage to the compressor clutch.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule:
- Importance: Adhering to the recommended maintenance schedule provided by your vehicle’s manufacturer is crucial for the longevity of the AC system.
- Typical Maintenance Tasks:
- Checking and lubricating the AC compressor clutch.
- Inspecting belts and hoses.
- Flushing the AC system.
- Benefits: Ensuring the AC system is properly maintained.
- Avoid Overloading the System:
- Why: Excessive use of the air conditioning system, especially under extreme conditions, can put stress on the AC compressor clutch.
- How to Avoid Overloading:
- Use the AC system judiciously.
- Avoid running it at maximum settings for prolonged periods.
- Use the recirculation mode to reduce the load on the AC system.
- Benefits: Reducing stress on the AC compressor clutch and prolonging its lifespan.
- Protect Electrical Connections:
- Importance: Ensuring that the electrical connections related to the AC compressor clutch are secure and free from corrosion.
- Maintenance Tasks:
- Inspect these connections during routine maintenance.
- Clean corroded terminals with a wire brush.
- Apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
- Ensure connections are adequately insulated.
- Benefits: Preventing electrical issues that can affect the clutch’s operation.
8. Why Is Rapid Cycling A Sign Of A Faulty AC Compressor Clutch?
Rapid cycling, where the AC compressor engages and disengages frequently, indicates a problem with the clutch or other components, such as low refrigerant levels or a clogged expansion valve. This frequent start-stop action can damage the clutch over time.
Rapid cycling of the AC compressor clutch is a significant indicator of underlying issues within the air conditioning system. Understanding why this occurs can help you diagnose and address the root cause effectively.
- What is Rapid Cycling?
- Rapid cycling refers to the AC compressor engaging and disengaging more frequently than normal. Typically, a properly functioning AC compressor should cycle on and off at regular intervals to maintain the desired cabin temperature.
- When the compressor cycles rapidly, it turns on and off in short bursts, often within seconds or minutes, instead of longer, more consistent intervals.
- Reasons for Rapid Cycling:
- Low Refrigerant Levels: Insufficient refrigerant is one of the most common causes of rapid cycling.
- When the refrigerant level is low, the low-pressure switch detects this condition and disengages the compressor to prevent damage.
- As the pressure equalizes, the switch may re-engage the compressor, leading to a short cycle.
- Clogged Expansion Valve: A clogged or restricted expansion valve can also cause rapid cycling.
- The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator. If it’s clogged, the refrigerant flow is reduced, leading to low pressure and the compressor disengaging.
- Faulty Pressure Switches: Malfunctioning pressure switches can send incorrect signals to the compressor, causing it to cycle rapidly.
- A faulty low-pressure switch may disengage the compressor even when the refrigerant level is adequate.
- A faulty high-pressure switch may disengage the compressor prematurely, even if the high-side pressure is not excessively high.
- Electrical Issues: Problems with the electrical system can also contribute to rapid cycling.
- Loose or corroded wiring connections can cause intermittent signals to the compressor clutch, leading to frequent engagement and disengagement.
- A faulty relay can also cause the compressor to cycle rapidly.
- Overcharged System: Although less common, an overcharged system can also cause rapid cycling.
- Excessive refrigerant can lead to high pressures, causing the high-pressure switch to disengage the compressor.
- Low Refrigerant Levels: Insufficient refrigerant is one of the most common causes of rapid cycling.
- Impact on the AC Compressor Clutch:
- Increased Wear and Tear: Rapid cycling puts additional stress on the AC compressor clutch, leading to increased wear and tear.
- The frequent engagement and disengagement cause the clutch to work harder and generate more heat, which can accelerate wear.
- Reduced Lifespan: The increased wear and tear can significantly reduce the lifespan of the AC compressor clutch.
- Premature failure of the clutch can result in costly repairs.
- Inefficient Cooling: Rapid cycling reduces the overall efficiency of the AC system.
- The frequent starts and stops prevent the compressor from maintaining a consistent cooling output, resulting in less effective cooling performance.
- Increased Wear and Tear: Rapid cycling puts additional stress on the AC compressor clutch, leading to increased wear and tear.
9. How Can DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN Help Me Diagnose AC Compressor Clutch Issues?
DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training on automotive diagnostics, including AC systems. Our courses cover in-depth knowledge of diagnostic tools, software applications, and troubleshooting techniques, enhancing your skills in identifying and resolving AC compressor clutch problems efficiently. With our training, you’ll be well-equipped to handle complex diagnostic scenarios.
DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing top-tier education and resources to automotive technicians. Here’s how we can assist you in diagnosing AC compressor clutch issues:
- Comprehensive Training Programs:
- Diagnostic Fundamentals: Our courses cover the core principles of automotive diagnostics, including electrical systems, sensor operation, and data analysis.
- Advanced AC System Diagnostics: We offer specialized training on AC systems, focusing on the intricacies of compressor clutch operation, refrigerant management, and component testing.
- Hands-On Experience: Our training programs include hands-on exercises using real vehicles and diagnostic tools, allowing you to apply your knowledge in a practical setting.
- Expert Instructors:
- Industry Professionals: Our instructors are experienced automotive technicians and diagnostic specialists with extensive knowledge of AC systems.
- Personalized Support: We provide personalized support and guidance to help you master diagnostic techniques and troubleshoot complex issues.
- Cutting-Edge Resources:
- Diagnostic Software: We offer training on the latest diagnostic software and tools, including scan tools, multimeters, and pressure gauges.
- Online Resources: Our online portal provides access to a wealth of resources, including training videos, diagnostic guides, and technical documentation.
- Certification Programs:
- Industry-Recognized Certifications: Upon completion of our training programs, you can earn industry-recognized certifications that demonstrate your expertise in AC system diagnostics.
- Community Support:
- Networking Opportunities: Connect with other automotive technicians and diagnostic specialists through our online forum and networking events.
- Collaborative Learning: Share your experiences and learn from others in the field, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
- Specific Diagnostic Skills:
- Electrical Diagnostics: Learn how to use a multimeter to check for power, ground, and continuity in the compressor clutch circuit.
- Sensor Testing: Master the techniques for testing pressure and temperature sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Data Analysis: Develop the skills to interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and analyze sensor data to identify the root cause of AC system problems.
- Preventive Maintenance Strategies:
- Inspection Techniques: Learn how to perform thorough inspections of the AC compressor clutch and system components.
- Maintenance Procedures: Understand the importance of regular maintenance, such as cleaning, lubrication, and refrigerant level checks.
10. What Are The Benefits Of Maintaining A Functional AC Compressor Clutch?
Maintaining a functional AC compressor clutch ensures a comfortable driving experience, prevents further damage to the AC system, and avoids costly repairs. Proper maintenance also enhances the vehicle’s resale value.
Maintaining a functional AC compressor clutch offers numerous benefits that extend beyond mere comfort. Here are the key advantages:
- Enhanced Driving Comfort:
- Consistent Cooling: A properly functioning AC compressor clutch ensures consistent cooling performance, maintaining a comfortable cabin temperature regardless of external conditions.
- Reduced Humidity: The AC system also removes humidity from the cabin, preventing fogging of windows and enhancing visibility.
- Prevention of Further Damage:
- Compressor Protection: A malfunctioning clutch can cause the compressor to work harder, leading to overheating and potential damage. Maintaining the clutch helps protect the compressor from premature failure.
- System Integrity: Addressing clutch issues promptly can prevent damage to other components in the AC system, such as the evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve.
- Cost Savings:
- Reduced Repair Costs: Regular maintenance and timely repairs can prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems, saving you money on costly repairs.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: A properly functioning AC system can improve fuel efficiency by reducing the load on the engine.
- Extended Lifespan of AC System:
- Component Longevity: By maintaining the AC compressor clutch and other components, you can extend the overall lifespan of the AC system.
- System Reliability: A well-maintained AC system is more reliable and less prone to breakdowns, ensuring consistent performance over time.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Reduced Refrigerant Leaks: A properly maintained AC system is less likely to leak refrigerant, which is a harmful greenhouse gas.
- Energy Efficiency: An efficient AC system consumes less energy, reducing the vehicle’s carbon footprint.
- Improved Vehicle Resale Value:
- Attractiveness to Buyers: A well-maintained AC system is an attractive feature for potential buyers, increasing the vehicle’s resale value.
- Demonstration of Care: Regular maintenance records demonstrate that the vehicle has been well cared for, instilling confidence in buyers.
- Prevention of Overheating:
- Engine Cooling: The AC system indirectly contributes to engine cooling by removing heat from the engine compartment.
- Reduced Strain on Engine: A properly functioning AC system reduces the strain on the engine, preventing overheating and potential damage.
Are you ready to elevate your automotive diagnostic skills and master AC system troubleshooting? Visit DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive training programs, cutting-edge resources, and expert guidance. Contact us at Address: 275 N Harrison St, Chandler, AZ 85225, United States, or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Let DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN be your partner in achieving automotive excellence. Discover how to use car diagnostic tools and software to resolve car electrical problems!
FAQ About AC Compressor Clutch Diagnosis
-
What tools do I need to diagnose an AC compressor clutch issue?
You’ll need a multimeter, a set of feeler gauges, a socket set, a wrench set, and the vehicle’s service manual. A scan tool can also be helpful for reading diagnostic trouble codes.
-
How do I know if my AC compressor clutch is engaging at all?
Visually inspect the clutch when the AC is turned on. The clutch plate should spin along with the pulley. If it doesn’t, the clutch is not engaging.
-
Can low refrigerant cause the AC compressor clutch not to engage?
Yes, low refrigerant levels can prevent the clutch from engaging due to the low-pressure switch preventing operation to protect the compressor.
-
Is it possible to replace just the AC compressor clutch, or do I need to replace the entire compressor?
In many cases, you can replace just the clutch. However, it depends on the vehicle and the availability of the clutch as a separate part.
-
What is the correct air gap for an AC compressor clutch?
The correct air gap varies by vehicle. Consult your vehicle’s service manual for the specific measurement, typically between 0.020″ and 0.040″.
-
What does it mean if my AC compressor clutch is making a squealing noise?
A squealing noise often indicates a worn or glazed clutch plate, a loose belt, or a misaligned pulley.
-
How do I check the electrical connections to the AC compressor clutch?
Inspect the wiring for damage, corrosion, or looseness. Use a multimeter to check for proper voltage and ground at the connector.
-
What is a clutch relay, and how do I test it?
The clutch relay is an electrical switch that controls power to the AC compressor clutch. You can test it using a multimeter to check for continuity and proper operation when voltage is applied.
-
Can a faulty pressure switch cause the AC compressor clutch not to engage?
Yes, a faulty pressure switch can prevent the clutch from engaging by sending incorrect signals to the compressor.
-
Where can I find reliable information about AC compressor clutch diagnosis and repair?
You can find reliable information in your vehicle’s service manual, reputable online automotive forums, and training resources like those offered by DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN.
