DTS Monaco is a powerful tool for ECU programming, but interruptions can occur. This article from DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN will explore how DTS Monaco handles ECU programming interruptions and potential recovery, offering solutions to ensure a smooth car coding experience. Dive in to discover how to keep your car coding skills sharp and your projects running smoothly with advanced diagnostic procedures and car software solutions.
Contents
- 1. Understanding ECU Programming with DTS Monaco
- 2. Common Causes of Interruptions During ECU Programming
- 3. How DTS Monaco Detects and Responds to Interruptions
- 4. Automatic Recovery Features in DTS Monaco
- 5. Manual Recovery Procedures Using DTS Monaco
- 6. Best Practices to Prevent Interruptions During ECU Programming
- 7. Troubleshooting Common Errors During Recovery
- 8. Advanced Techniques for Complex Recovery Scenarios
- 9. The Role of Seed Key Calculators in Recovery
Table of Contents
- Understanding ECU Programming with DTS Monaco
- Common Causes of Interruptions During ECU Programming
- How DTS Monaco Detects and Responds to Interruptions
- Automatic Recovery Features in DTS Monaco
- Manual Recovery Procedures Using DTS Monaco
- Best Practices to Prevent Interruptions During ECU Programming
- Troubleshooting Common Errors During Recovery
- Advanced Techniques for Complex Recovery Scenarios
- The Role of Seed Key Calculators in Recovery
- Ensuring Data Integrity and Security During Recovery
- Training and Resources Available at DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN
- FAQ: Addressing Common Questions About DTS Monaco and ECU Programming Recovery
1. Understanding ECU Programming with DTS Monaco
What is ECU programming with DTS Monaco and why is it essential?
ECU programming with DTS Monaco is the process of modifying or updating the software within a vehicle’s Electronic Control Units (ECUs) using the DTS Monaco software, which is essential for customizing vehicle functions, improving performance, and addressing software-related issues. DTS Monaco is used by automotive technicians, engineers, and car enthusiasts to perform tasks such as variant coding, retrofitting options, and flashing new software onto ECUs, thereby unlocking hidden features and optimizing vehicle performance. This detailed control is vital for modern vehicle maintenance and customization.
DTS Monaco, or Diagnostic Tool Set Monaco, is a sophisticated software solution used primarily for engineering, testing, and diagnosing automotive ECUs. Developed by Daimler AG, it allows users to communicate directly with the ECUs in a vehicle, read and write data, and perform advanced diagnostic procedures. Unlike simpler diagnostic tools, DTS Monaco provides a deep level of access and control, making it essential for tasks beyond basic error code reading and clearing.
-
Key Capabilities:
- ECU Flashing: Updating the software on an ECU to the latest version.
- Variant Coding: Customizing vehicle functions by changing parameters within the ECU.
- Retrofitting: Adding new features to a vehicle by enabling the necessary software functions in the ECU.
- Diagnostics: Identifying and troubleshooting complex issues by reading data from the ECU.
- Data Logging: Recording ECU data for analysis and optimization.
-
Why DTS Monaco is Essential:
- Customization: DTS Monaco allows technicians to tailor vehicle settings to specific customer preferences, unlocking features like enhanced driving modes or personalized comfort settings.
- Performance Enhancement: By optimizing ECU parameters, technicians can improve vehicle performance, such as increasing horsepower or improving fuel efficiency.
- Software Updates: Keeping ECU software up-to-date ensures that vehicles operate with the latest improvements and bug fixes, enhancing reliability and longevity.
- Advanced Diagnostics: DTS Monaco enables in-depth analysis of ECU data, helping diagnose and resolve complex issues that standard diagnostic tools might miss.
-
Use Cases:
- Disabling Start/Stop Systems: Many users want to disable the automatic start/stop function, which can be achieved through variant coding with DTS Monaco.
- Activating Hidden Features: Enabling features like cornering lights or enhanced instrument cluster displays.
- Retrofitting Components: Adding new hardware components, such as a rearview camera, and configuring the ECU to recognize and utilize the new hardware.
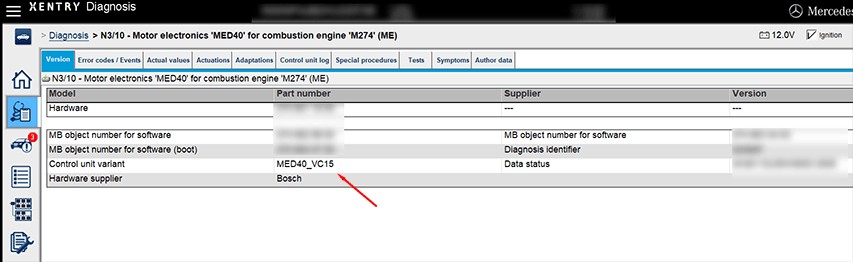 Mercedes XENTRY Diagnosis Screen
Mercedes XENTRY Diagnosis Screen
2. Common Causes of Interruptions During ECU Programming
What are the common reasons for interruptions during ECU programming?
Interruptions during ECU programming are commonly caused by power failures, communication errors, software glitches, and hardware issues, any of which can disrupt the data transfer and potentially harm the ECU, making stable power supply and reliable connections essential. These interruptions can lead to incomplete updates or corrupted data, requiring careful management and recovery strategies.
ECU programming is a sensitive process that requires a stable and uninterrupted connection between the programming tool and the vehicle’s ECU. Unfortunately, several factors can cause interruptions, leading to potential issues. Understanding these common causes is crucial for preventing them and ensuring a smooth programming experience.
-
Power Failures:
- Vehicle Battery Issues: A weak or dying vehicle battery is a frequent cause of interruptions. During programming, the ECU requires a consistent power supply, and fluctuations in voltage can halt the process.
- Impact: Incomplete data transfer, ECU corruption.
- Prevention: Ensure the vehicle battery is fully charged or use a battery maintainer during programming.
- External Power Supply Interruption: If using an external power supply, any disruption to the power source can interrupt the programming process.
- Impact: Data loss, ECU damage.
- Prevention: Use a reliable power supply and ensure it is securely connected.
- Vehicle Battery Issues: A weak or dying vehicle battery is a frequent cause of interruptions. During programming, the ECU requires a consistent power supply, and fluctuations in voltage can halt the process.
-
Communication Errors:
- Cable Disconnections: Loose or damaged cables can cause intermittent disconnections, disrupting communication between the programming tool and the ECU.
- Impact: Failed programming attempts, ECU errors.
- Prevention: Use high-quality cables and ensure they are securely connected to both the vehicle and the programming tool.
- Adapter Issues: Problems with the J2534 pass-thru adapter, such as driver conflicts or hardware malfunctions, can lead to communication errors.
- Impact: Inability to communicate with the ECU, programming failures.
- Prevention: Keep adapter drivers up-to-date and use a reliable adapter recommended by DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN.
- Network Interruptions: For vehicles that require online programming or authentication, interruptions in the internet connection can halt the process.
- Impact: Programming timeouts, incomplete updates.
- Prevention: Use a stable and reliable internet connection.
- Cable Disconnections: Loose or damaged cables can cause intermittent disconnections, disrupting communication between the programming tool and the ECU.
-
Software Glitches:
- DTS Monaco Software Errors: Bugs or glitches within the DTS Monaco software can sometimes cause interruptions.
- Impact: Unexpected program termination, data corruption.
- Prevention: Keep DTS Monaco updated to the latest version and ensure your computer meets the recommended system requirements.
- Driver Conflicts: Conflicts between different software drivers on your computer can interfere with DTS Monaco’s ability to communicate with the ECU.
- Impact: Communication errors, software instability.
- Prevention: Ensure all drivers are compatible and up-to-date, and avoid installing unnecessary software.
- DTS Monaco Software Errors: Bugs or glitches within the DTS Monaco software can sometimes cause interruptions.
-
Hardware Issues:
- ECU Malfunctions: In rare cases, the ECU itself may have internal issues that cause it to become unresponsive during programming.
- Impact: Programming failures, potential ECU damage.
- Prevention: Ensure the ECU is in good working condition before attempting to program it.
- Laptop Problems: Overheating, hardware failures, or system crashes on the laptop running DTS Monaco can interrupt the programming process.
- Impact: Data loss, incomplete programming.
- Prevention: Use a reliable laptop that meets DTS Monaco’s system requirements, and ensure it is properly maintained.
- ECU Malfunctions: In rare cases, the ECU itself may have internal issues that cause it to become unresponsive during programming.
By identifying and addressing these common causes of interruptions, technicians can significantly reduce the risk of programming failures and ensure a more reliable and efficient ECU programming experience. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers resources and training to help you navigate these challenges effectively.
3. How DTS Monaco Detects and Responds to Interruptions
How does DTS Monaco identify and react to interruptions during ECU programming?
DTS Monaco detects interruptions during ECU programming through error messages, communication timeouts, and diagnostic checks, responding by halting the current process, logging the error, and prompting the user to take corrective action, which usually involves restarting the procedure or recovering the ECU’s previous state. This proactive approach helps prevent further damage and ensures a structured recovery process.
DTS Monaco is designed with built-in mechanisms to detect and respond to interruptions during ECU programming. These mechanisms help to prevent data corruption and minimize potential damage to the ECU. Here’s how DTS Monaco handles such situations:
-
Real-Time Monitoring:
- Communication Checks: DTS Monaco continuously monitors the communication channel between the software and the ECU. It sends regular requests and expects timely responses.
- Data Integrity: The software performs checksums and other data integrity checks to ensure that the data being transferred is accurate and complete.
-
Detection Methods:
- Timeout Detection: If the ECU fails to respond within a specified time frame, DTS Monaco detects a communication timeout. This can indicate a disconnection, ECU unresponsiveness, or other communication issues.
- Error Messages: The ECU may send error messages to DTS Monaco if it encounters problems during the programming process. These messages provide valuable information about the nature of the interruption.
- Diagnostic Checks: DTS Monaco runs periodic diagnostic checks to verify the status of the ECU and the stability of the connection.
-
Responses to Interruptions:
- Immediate Halt: Upon detecting an interruption, DTS Monaco immediately halts the programming process to prevent further data corruption.
- Error Logging: The software logs the error, including the time of occurrence, the nature of the error, and any relevant diagnostic information. This log is crucial for troubleshooting and recovery.
- User Notification: DTS Monaco displays a notification to the user, explaining the nature of the interruption and recommending possible corrective actions. This could include checking the cable connections, verifying the power supply, or restarting the ECU.
-
Example Scenario:
- Interruption: A technician is flashing new software onto an ECU when a power surge occurs, causing a momentary loss of power.
- Detection: DTS Monaco detects the interruption through a communication timeout and an error message from the ECU.
- Response:
- DTS Monaco immediately stops the flashing process.
- The software logs the error, noting the time and the specific error code received from the ECU.
- A pop-up message appears on the technician’s screen: “ECU programming interrupted. Communication timeout detected. Please check power supply and cable connections.”
-
Best Practices:
- Stable Power Supply: Always use a stable power supply or battery maintainer during ECU programming to prevent power-related interruptions.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all cable connections are secure and in good condition.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep an eye on the DTS Monaco interface during programming to quickly identify and respond to any error messages or warnings.
By employing these detection and response mechanisms, DTS Monaco helps to mitigate the risks associated with interruptions during ECU programming, providing a safer and more reliable experience. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training on how to effectively use these features and handle various interruption scenarios.
4. Automatic Recovery Features in DTS Monaco
Are there automatic recovery options in DTS Monaco?
Yes, DTS Monaco includes automatic recovery features like rollback to previous configurations and automated re-flashing attempts, designed to restore the ECU to a functional state after an interruption, making it easier for technicians to manage issues without extensive manual intervention. These features are crucial for minimizing downtime and preventing permanent damage.
DTS Monaco is equipped with several automatic recovery features that help restore the ECU to a functional state after an interruption. These features are designed to minimize downtime and prevent permanent damage. Here are some of the key automatic recovery options available in DTS Monaco:
-
Rollback to Previous Configuration:
- Functionality: DTS Monaco automatically creates a backup of the ECU’s current configuration before initiating any programming changes. In the event of an interruption, the software can roll back to this previous configuration, restoring the ECU to its original state.
- Benefits: This feature is particularly useful when a programming attempt fails midway, preventing the ECU from being left in an unstable or non-functional state.
- How it Works:
- Before starting the programming process, DTS Monaco reads and saves the existing ECU configuration.
- If an interruption occurs, the software detects the error and initiates the rollback process.
- DTS Monaco writes the saved configuration data back to the ECU, effectively undoing any incomplete changes.
-
Automated Re-Flashing Attempts:
- Functionality: If a flashing process is interrupted, DTS Monaco can automatically attempt to re-flash the ECU. This is useful for recovering from incomplete or corrupted software updates.
- Benefits: Reduces the need for manual intervention, saving time and minimizing the risk of human error.
- How it Works:
- DTS Monaco detects that the flashing process has been interrupted.
- The software automatically restarts the flashing process from the beginning or from the point of interruption, depending on the nature of the error.
- DTS Monaco repeats the flashing process until it is successfully completed or until a predefined number of attempts have been made.
-
Error Correction Codes (ECC):
- Functionality: DTS Monaco uses ECC to detect and correct errors during data transfer. This helps to ensure that the data written to the ECU is accurate and complete.
- Benefits: Reduces the risk of data corruption and improves the reliability of the programming process.
- How it Works:
- As data is being transferred, ECC algorithms add redundant information that can be used to detect and correct errors.
- If an error is detected, the ECC algorithms automatically correct the error without interrupting the programming process.
-
Example Scenario:
- Interruption: A technician is updating the ECU software when a cable becomes disconnected, interrupting the flashing process.
- Automatic Recovery:
- DTS Monaco detects the interruption and initiates the rollback process, restoring the ECU to its previous configuration.
- The software then automatically attempts to re-flash the ECU, ensuring that the software update is successfully completed.
-
Best Practices:
- Enable Automatic Recovery: Ensure that the automatic recovery features are enabled in DTS Monaco’s settings.
- Monitor the Process: Keep an eye on the programming process to quickly identify any issues and ensure that the automatic recovery features are working as expected.
- Review Logs: After an interruption, review the DTS Monaco logs to understand the nature of the error and verify that the automatic recovery process was successful.
By leveraging these automatic recovery features, technicians can significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of ECU programming with DTS Monaco. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers detailed training on how to configure and use these features to their full potential.
5. Manual Recovery Procedures Using DTS Monaco
When are manual recovery procedures necessary with DTS Monaco?
Manual recovery procedures are necessary when automatic recovery fails or when dealing with complex issues such as corrupted flash memory or unresponsive ECUs, requiring technicians to use specific DTS Monaco functions to diagnose, re-flash, and restore the ECU to a working state, ensuring a comprehensive approach to ECU repair. These procedures demand a deeper understanding of the software and ECU architecture.
While DTS Monaco offers several automatic recovery features, there are situations where manual recovery procedures are necessary. These procedures require a deeper understanding of the software and ECU architecture. Here are some scenarios where manual recovery is needed and the steps to perform them:
-
When Automatic Recovery Fails:
- Scenario: The automatic rollback or re-flashing attempts fail to restore the ECU to a functional state.
- Cause: The interruption may have caused significant data corruption, or the automatic recovery mechanisms may be insufficient to address the specific issue.
-
Complex Issues:
- Scenario: Dealing with corrupted flash memory or an unresponsive ECU.
- Cause: Severe data corruption, hardware issues, or firmware problems that require targeted intervention.
-
Manual Recovery Steps:
- Diagnosis:
- Use DTS Monaco to diagnose the ECU and identify the specific errors or issues.
- Check the ECU’s status and read any available diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Re-Flashing:
- Manually re-flash the ECU with a known good software version.
- Use the “Flash Programming” function in DTS Monaco to upload the correct firmware to the ECU.
- Variant Coding:
- After re-flashing, perform variant coding to ensure that the ECU is correctly configured for the vehicle.
- Use the “Variant Coding” function in DTS Monaco to set the appropriate parameters for the vehicle’s options and features.
- Manual Data Correction:
- In some cases, manual data correction may be necessary.
- Use DTS Monaco to read and modify specific memory locations within the ECU to correct corrupted data.
- Seed Key Calculator:
- For certain operations, you may need to use a seed key calculator to gain access to protected areas of the ECU.
- Use the seed key calculator to generate the appropriate key, and then enter it into DTS Monaco to unlock the necessary functions.
- Hard Reset:
- After making changes, perform a hard reset to ensure that the ECU reloads the new parameters.
- Use the “FN_HardReset” function in DTS Monaco to reset the ECU.
- Testing and Verification:
- After completing the recovery process, thoroughly test the ECU to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Use DTS Monaco to monitor the ECU’s performance and verify that all systems are working as expected.
- Diagnosis:
-
Example Scenario:
- Interruption: A technician is updating the ECU software when a power failure occurs, causing the automatic recovery to fail.
- Manual Recovery Process:
- The technician uses DTS Monaco to diagnose the ECU and identify the corrupted data.
- The technician manually re-flashes the ECU with the correct software version.
- The technician performs variant coding to configure the ECU for the vehicle.
- The technician uses a seed key calculator to unlock access to protected functions.
- The technician performs a hard reset to ensure that the ECU reloads the new parameters.
- The technician tests the ECU to verify that it is functioning correctly.
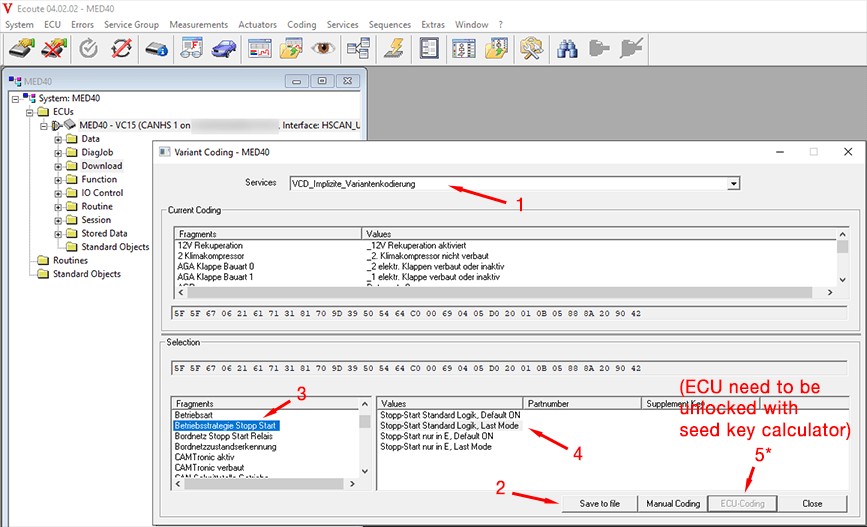 DTS Monaco ECU Selection
DTS Monaco ECU Selection
-
Best Practices:
- Detailed Documentation: Keep detailed records of all recovery steps taken, including the specific software versions used, the parameters changed, and any error messages encountered.
- Backup: Always create a backup of the ECU’s configuration before attempting any manual recovery procedures.
- Expert Guidance: Seek guidance from experienced technicians or DTS Monaco experts when performing complex recovery procedures.
- Training: Get comprehensive training on DTS Monaco’s manual recovery features to ensure you have the skills and knowledge needed to handle a wide range of issues.
By mastering these manual recovery procedures, technicians can effectively address complex ECU issues and ensure the long-term reliability of vehicle systems. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN provides advanced training and resources to help you become proficient in manual ECU recovery.
6. Best Practices to Prevent Interruptions During ECU Programming
What are the recommended practices to avoid interruptions during ECU programming?
To prevent interruptions during ECU programming, ensure a stable power supply, use high-quality cables, maintain a reliable internet connection, keep software updated, and disable unnecessary programs, all of which contribute to a stable and secure programming environment, reducing the risk of data corruption and ECU damage. These practices are essential for maintaining efficiency and reliability.
Preventing interruptions during ECU programming is crucial for ensuring a smooth and successful process. Here are some best practices to minimize the risk of interruptions:
-
Stable Power Supply:
- Vehicle Battery Maintenance:
- Ensure the vehicle battery is fully charged and in good condition.
- Use a battery maintainer or charger to provide a consistent power supply during programming.
- External Power Supply:
- If using an external power supply, ensure it is reliable and provides the correct voltage and amperage.
- Use a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) to protect against power outages.
- Vehicle Battery Maintenance:
-
High-Quality Cables and Connections:
- Cable Quality:
- Use high-quality cables that are designed for ECU programming.
- Avoid using damaged or worn cables.
- Secure Connections:
- Ensure that all cable connections are secure and properly seated.
- Check the connections regularly during the programming process.
- Cable Quality:
-
Reliable Internet Connection:
- Stable Connection:
- Use a stable and reliable internet connection, especially for online programming or authentication.
- Avoid using Wi-Fi if possible; a wired connection is more stable.
- Minimize Network Activity:
- Close any unnecessary programs or applications that may consume bandwidth and cause network interruptions.
- Stable Connection:
-
Software and Driver Updates:
- DTS Monaco Updates:
- Keep DTS Monaco updated to the latest version.
- Install any available patches or hotfixes.
- Driver Updates:
- Ensure that all drivers, including the J2534 pass-thru adapter drivers, are up-to-date.
- Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest drivers.
- DTS Monaco Updates:
-
Disable Unnecessary Programs:
- Close Applications:
- Close any unnecessary programs or applications running on your computer.
- These programs can consume system resources and cause conflicts.
- Disable Antivirus Software:
- Temporarily disable antivirus software, as it can sometimes interfere with the programming process.
- Ensure that you re-enable the antivirus software after programming is complete.
- Close Applications:
-
Proper Hardware Configuration:
- Laptop Specifications:
- Use a laptop that meets the recommended system requirements for DTS Monaco.
- Ensure the laptop has sufficient RAM, processing power, and storage space.
- Laptop Maintenance:
- Keep the laptop clean and free of dust.
- Avoid overheating by ensuring proper ventilation.
- Laptop Specifications:
-
Regular System Checks:
- Pre-Programming Checks:
- Before starting the programming process, perform a thorough system check.
- Verify that all components are functioning correctly.
- Diagnostic Scans:
- Run a diagnostic scan of the vehicle to identify any potential issues.
- Address any issues before attempting to program the ECU.
- Pre-Programming Checks:
-
Example Scenario:
- Preparation: A technician is preparing to update the ECU software on a Mercedes-Benz vehicle.
- Preventive Measures:
- The technician uses a battery maintainer to ensure a stable power supply.
- The technician checks the cable connections to ensure they are secure.
- The technician connects the laptop to the internet using a wired connection.
- The technician updates DTS Monaco to the latest version and installs the latest drivers for the J2534 adapter.
- The technician closes all unnecessary programs and disables the antivirus software.
- The technician performs a diagnostic scan of the vehicle to identify any potential issues.
By following these best practices, technicians can significantly reduce the risk of interruptions during ECU programming, ensuring a more reliable and efficient process. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources and training to help you implement these practices effectively.
7. Troubleshooting Common Errors During Recovery
What are the common errors that occur during ECU recovery and how can they be fixed?
Common errors during ECU recovery include communication failures, incorrect seed key entries, and software incompatibilities, which can be resolved by verifying connections, using correct seed keys, updating software, and ensuring compatibility, highlighting the importance of meticulous troubleshooting and up-to-date resources for successful ECU restoration. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers extensive support to navigate these challenges.
Even with the best preventive measures, errors can still occur during ECU recovery. Troubleshooting these errors effectively is crucial for restoring the ECU to a functional state. Here are some common errors and their solutions:
-
Communication Failures:
- Error: “Communication timeout,” “ECU not responding,” or similar messages indicating a loss of communication between DTS Monaco and the ECU.
- Causes:
- Loose or damaged cable connections.
- Incorrect J2534 pass-thru adapter configuration.
- ECU unresponsiveness.
- Solutions:
- Check Cable Connections: Ensure that all cable connections are secure and properly seated.
- Verify Adapter Configuration: Ensure that the J2534 pass-thru adapter is correctly configured in DTS Monaco. Check the adapter’s driver status in Device Manager.
- Restart ECU: Try restarting the ECU by disconnecting and reconnecting the vehicle battery.
- Test with Another ECU: If possible, test the adapter and DTS Monaco with another ECU to rule out hardware issues.
-
Incorrect Seed Key Entries:
- Error: “Security access denied,” “Invalid seed key,” or similar messages indicating that the seed key entered is incorrect.
- Causes:
- Incorrect seed key calculator settings.
- Wrong DLL file selected in the seed key calculator.
- Typographical errors when entering the seed key in DTS Monaco.
- Solutions:
- Verify Seed Key Calculator Settings: Ensure that the seed key calculator is configured correctly for the specific ECU and access level.
- Select Correct DLL File: Ensure that the correct DLL file is selected in the seed key calculator. Refer to the ECU documentation or online resources for the correct DLL.
- Double-Check Seed Key Entry: Double-check the seed key entered in DTS Monaco for any typographical errors.
- Try Again: Sometimes, the seed key generation process can fail. Try generating the seed key again and re-enter it in DTS Monaco.
-
Software Incompatibilities:
- Error: “Incompatible software version,” “Missing CBF file,” or similar messages indicating that the software version is not compatible with the ECU.
- Causes:
- Using an outdated version of DTS Monaco.
- Missing or corrupted CBF (Container Binary Format) files.
- Incorrect software version selected for the ECU.
- Solutions:
- Update DTS Monaco: Ensure that DTS Monaco is updated to the latest version.
- Verify CBF Files: Verify that the required CBF files are present in the correct directory. If necessary, download the CBF files from a trusted source and place them in the appropriate folder.
- Select Correct Software Version: Ensure that the correct software version is selected for the ECU in DTS Monaco. Refer to the ECU documentation or online resources for the correct software version.
-
Flash Programming Errors:
- Error: “Flash programming failed,” “Write error,” or similar messages indicating that the flash programming process has failed.
- Causes:
- Interrupted power supply during flashing.
- Communication errors during flashing.
- Incorrect flash data.
- Solutions:
- Ensure Stable Power Supply: Ensure that the vehicle has a stable power supply during flashing. Use a battery maintainer or charger.
- Check Cable Connections: Check all cable connections to ensure they are secure.
- Verify Flash Data: Verify that the flash data is correct and not corrupted. Download the flash data from a trusted source.
- Retry Flashing: Retry the flashing process. Sometimes, a second attempt can be successful.
-
Example Scenario:
- Error: A technician is attempting to recover an ECU after a failed flash programming attempt and encounters a “Communication timeout” error.
- Troubleshooting Steps:
- The technician checks the cable connections and ensures they are secure.
- The technician verifies that the J2534 pass-thru adapter is correctly configured in DTS Monaco.
- The technician restarts the ECU by disconnecting and reconnecting the vehicle battery.
- After performing these steps, the communication is restored, and the technician can proceed with the recovery process.
By systematically troubleshooting these common errors, technicians can effectively recover ECUs and minimize downtime. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers detailed guides and support to help you navigate these challenges and ensure successful ECU recovery.
8. Advanced Techniques for Complex Recovery Scenarios
What advanced methods can be used for ECU recovery in challenging situations?
In complex ECU recovery scenarios, advanced techniques include direct memory editing, JTAG programming, and chip-off data recovery, which are used when standard methods fail, requiring specialized tools and expertise to bypass damaged or locked systems, ensuring data extraction and reprogramming for comprehensive ECU restoration. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN provides training to master these intricate procedures.
When standard recovery methods fail, advanced techniques may be necessary to restore an ECU. These techniques require specialized tools, expertise, and a deep understanding of ECU architecture. Here are some advanced methods for complex recovery scenarios:
-
Direct Memory Editing:
- What It Is: Direct memory editing involves reading and modifying the ECU’s memory contents directly, bypassing the standard communication interfaces.
- When to Use: This technique is used when the ECU is partially functional but has corrupted data that prevents it from booting or communicating properly.
- Tools Required:
- Memory reader/writer (e.g., BDM100, XPROG)
- Hex editor
- ECU memory map
- Procedure:
- Remove the ECU from the vehicle.
- Connect the memory reader/writer to the ECU’s memory chip.
- Read the memory contents and save them as a backup.
- Use a hex editor to identify and correct the corrupted data.
- Write the modified memory contents back to the ECU.
- Reinstall the ECU in the vehicle and test its functionality.
-
JTAG Programming:
- What It Is: JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) programming uses a hardware interface to directly access the ECU’s processor and memory.
- When to Use: This technique is used when the ECU is completely unresponsive or has a damaged bootloader.
- Tools Required:
- JTAG programmer (e.g., J-Link, Segger)
- JTAG adapter
- ECU JTAG pinout
- Procedure:
- Remove the ECU from the vehicle.
- Identify the JTAG pins on the ECU and connect the JTAG adapter.
- Use the JTAG programmer to connect to the ECU’s processor.
- Erase the ECU’s flash memory.
- Program the ECU with a known good firmware image.
- Reinstall the ECU in the vehicle and test its functionality.
-
Chip-Off Data Recovery:
- What It Is: Chip-off data recovery involves physically removing the memory chip from the ECU and reading its contents using a specialized chip reader.
- When to Use: This technique is used when the ECU is severely damaged, and other recovery methods are not possible.
- Tools Required:
- Hot air rework station
- Chip reader (e.g., PC-3000 Flash, UFS Explorer)
- Microscope
- Procedure:
- Remove the ECU from the vehicle.
- Use a hot air rework station to carefully remove the memory chip from the ECU.
- Clean the chip and place it in the chip reader.
- Read the memory contents and save them as a backup.
- Analyze the data and repair any corruption.
- Write the repaired data to a new memory chip.
- Reinstall the new memory chip on the ECU.
- Reinstall the ECU in the vehicle and test its functionality.
-
Example Scenario:
- Problem: An ECU is completely unresponsive after a failed firmware update.
- Advanced Recovery:
- The technician removes the ECU from the vehicle and identifies the JTAG pins.
- The technician connects a JTAG programmer to the ECU and erases the flash memory.
- The technician programs the ECU with a known good firmware image using the JTAG programmer.
- The technician reinstalls the ECU in the vehicle and tests its functionality, successfully restoring the ECU.
By mastering these advanced techniques, technicians can tackle even the most challenging ECU recovery scenarios. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers specialized training and resources to help you develop the skills and knowledge needed to perform these procedures safely and effectively.
9. The Role of Seed Key Calculators in Recovery
Why are seed key calculators important for ECU recovery?
Seed key calculators are crucial for ECU recovery as they generate the necessary keys to unlock protected functions, allowing technicians to bypass security measures and perform critical operations like reflashing and variant coding, making them indispensable for accessing and restoring locked or protected ECUs. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training on using these tools effectively.
Seed key calculators play a vital role in ECU recovery by providing the necessary keys to unlock protected functions within the ECU. These functions are often required to perform critical operations such as reflashing, variant coding, and data correction. Here’s why seed key calculators are essential and how they are used in ECU recovery:
-
Understanding Seed Key Protection:
- Security Measures: Modern ECUs are equipped with security measures to prevent unauthorized access and modification of their software.
- Seed Key Exchange: To access protected functions, a seed key exchange is required. The ECU sends a “seed” value to the diagnostic tool, which must then use a seed key calculator to generate the correct “key” to unlock the function.
- Access Levels: Different functions require different access levels, each with its own unique seed key algorithm.
-
How Seed Key Calculators Work:
- Algorithm-Based Generation: Seed key calculators use complex algorithms to generate the correct key based on the seed value provided by the ECU and the specific access level required.
- DLL Files: Many seed key calculators rely on DLL (Dynamic Link Library) files that contain the specific algorithms used by different ECU manufacturers.
- User Input: The user inputs the seed value, selects the appropriate DLL file, and specifies the access level, and the calculator generates the corresponding key.
-
Importance in ECU Recovery:
- Bypassing Security: Seed key calculators allow technicians to bypass security measures and access protected functions required for ECU recovery.
- Reflashing: When an ECU is locked or corrupted, reflashing with a new software image is often necessary. Seed keys are required to unlock the flashing process.
- Variant Coding: After reflashing, variant coding is required to configure the ECU for the specific vehicle. Seed keys are needed to access the variant coding functions.
- Data Correction: In some cases, manual data correction is necessary to repair corrupted data within the ECU. Seed keys are required to unlock the memory locations that need to be modified.
-
Example Scenario:
- Problem: A technician needs to reflash an ECU after a failed software update, but the ECU is locked and requires a seed key to unlock the flashing process.
- Solution:
- The technician uses DTS Monaco to connect to the ECU and attempts to initiate the flashing process.
- The ECU sends a seed value to DTS Monaco.
- The technician opens the seed key calculator and enters the seed value.
- The technician selects the appropriate DLL file for the ECU.
- The technician specifies the required access level.
- The seed key calculator generates the corresponding key.
- The technician enters the key into DTS Monaco to unlock the flashing process.
- The technician successfully reflashes the ECU.
![Mercedes Seed Key Calculator](https://cimg4.ibsrv.