Diagnosing auxiliary battery issues using DTS Monaco is a valuable skill for automotive technicians, especially those focusing on car coding and advanced diagnostics. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and resources to master this process, enhancing your diagnostic capabilities and expanding your service offerings. Learning how to use DTS Monaco can also help you perform car coding and resolve complex issues efficiently, ensuring customer satisfaction and building your reputation as a skilled professional.
Contents
- 1. What is DTS Monaco and How Does it Aid in Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics?
- 1.1. Understanding the Role of the Auxiliary Battery
- 1.2. Why DTS Monaco is Essential for Accurate Diagnostics
- 2. Identifying the Need for Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics
- 3. Preparing for Diagnostics with DTS Monaco
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Auxiliary Battery Issues with DTS Monaco
- 4.1. Connect to the Vehicle
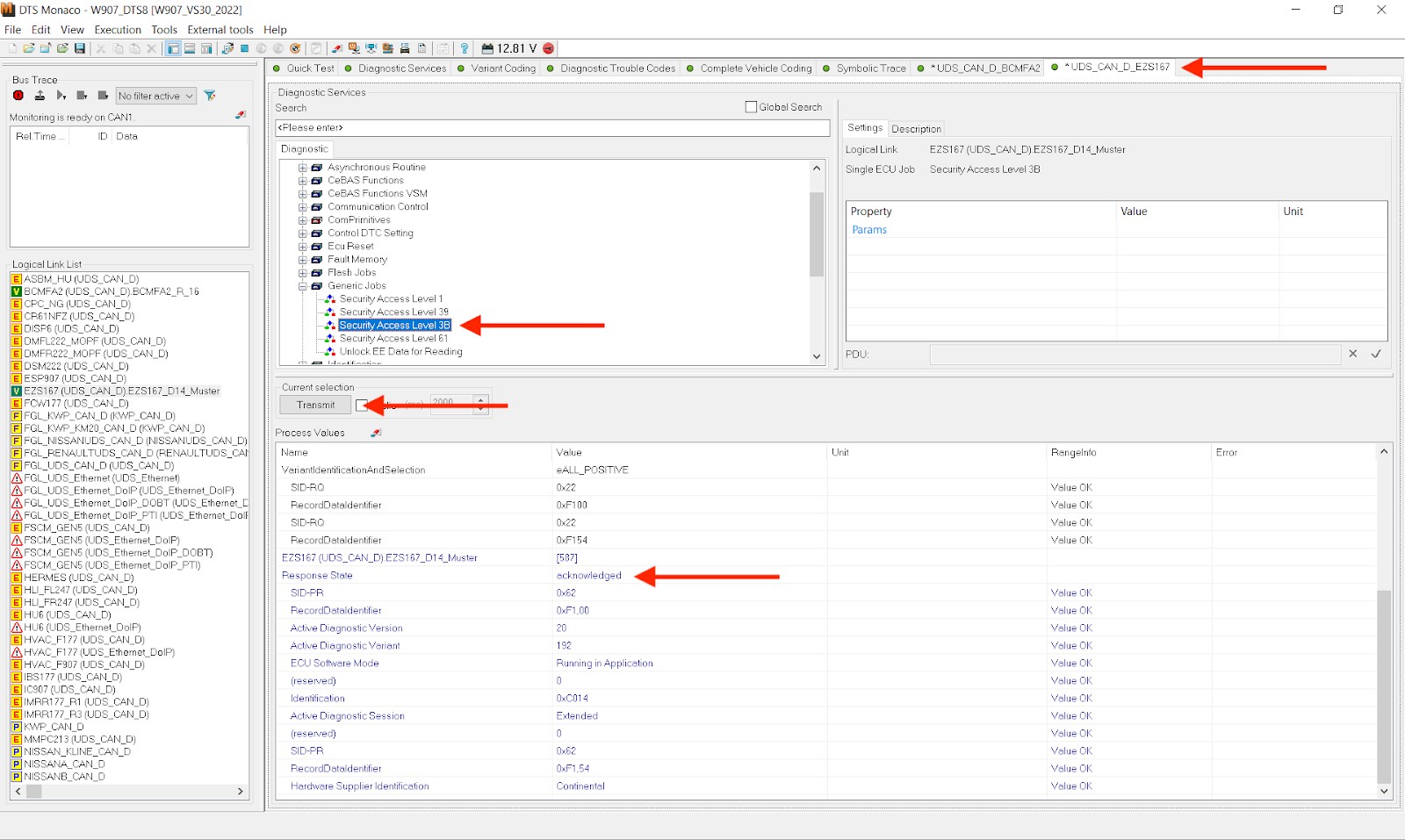
- 4.2. Access the Relevant ECU
- 4.3. Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4.4. Monitor Real-Time Data
- 4.5. Perform Guided Tests
- 4.6. Analyze the Results
- 4.7. Verify the Repair
- 5. Common Diagnostic Scenarios and Solutions
- 5.1. Low Voltage Issues
- 5.2. Charging Problems
- 5.3. Faulty Battery Sensors
- 5.4. Start-Stop System Issues
- 5.5. Communication Errors
- 6. Advanced Techniques for Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics
- 6.1. Component Testing
- 6.2. Circuit Analysis
- 6.3. Analyzing Wiring Diagrams
- 6.4. Using Oscilloscopes
- 7. Best Practices for Maintaining Auxiliary Batteries
- 7.1. Regular Voltage Checks
- 7.2. Proper Charging Habits
- 7.3. Clean Battery Terminals
- 7.4. Regular Load Tests
- 7.5. Avoid Extreme Temperatures
- 8. Car Coding and Auxiliary Battery Systems
- 8.1. Enabling and Disabling Features
- 8.2. Adjusting System Parameters
- 8.3. Recoding After Replacement
- 8.4. Customizing Power Management
- 9. Safety Precautions During Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics
- 9.1. Wear Protective Gear
- 9.2. Disconnect the Battery Properly
- 9.3. Work in a Well-Ventilated Area
- 9.4. Use Insulated Tools
- 9.5. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
- 10. Where to Find Training and Resources for DTS Monaco
1. What is DTS Monaco and How Does it Aid in Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics?
DTS Monaco is a diagnostic, testing, and engineering software used for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, allowing in-depth analysis and modification of electronic control units (ECUs). It aids in auxiliary battery diagnostics by providing access to real-time data, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and advanced testing routines that can pinpoint issues not detectable by standard OBD-II scanners.
DTS Monaco goes beyond basic error code reading; it facilitates direct communication with the vehicle’s ECUs. This allows technicians to monitor parameters like voltage, current, and temperature of the auxiliary battery in real-time. With these capabilities, you can observe the battery’s performance under various conditions, such as during start-up or when the vehicle’s electrical load changes. The ability to read and interpret DTCs specific to the auxiliary battery system is also crucial. These codes provide a starting point for diagnostics, often indicating the nature and location of the fault.
1.1. Understanding the Role of the Auxiliary Battery
The auxiliary battery supports functions such as start-stop systems and electronic accessories. It’s essential for maintaining vehicle performance and preventing unexpected failures.
The auxiliary battery in modern vehicles serves as a supplementary power source to support various electrical systems, especially during periods when the main battery is under heavy load or when the engine is temporarily off, such as during start-stop operation. According to a study by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), auxiliary batteries enhance the reliability and efficiency of vehicle electrical systems by ensuring a stable power supply to critical components. These batteries typically power systems like:
- Start-Stop System: The auxiliary battery ensures a smooth restart of the engine, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Electronic Accessories: It supports systems like infotainment, navigation, and other comfort features.
- Backup Power: In cases where the main battery voltage drops, the auxiliary battery can provide backup power to prevent system failures.
1.2. Why DTS Monaco is Essential for Accurate Diagnostics
DTS Monaco enables technicians to access specific diagnostic routines and parameters related to the auxiliary battery, providing more accurate and detailed information than generic scan tools. The software’s capabilities are paramount in diagnosing auxiliary battery issues because of its advanced functions. It can help with the following:
- Accessing Detailed Diagnostic Information: Unlike generic OBD-II scanners, DTS Monaco allows access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic codes and data related to the auxiliary battery system.
- Performing Advanced Testing: Technicians can conduct specific tests, such as load tests and voltage drop tests, directly through the software.
- Monitoring Real-Time Data: DTS Monaco provides real-time data monitoring of parameters like voltage, current, and temperature, helping identify anomalies.
- Recoding and Reprogramming: In some cases, the auxiliary battery system might require recoding or reprogramming after a battery replacement, which can be done using DTS Monaco.
2. Identifying the Need for Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics
Recognizing symptoms like start-stop system malfunctions or electrical issues is the first step. These can indicate problems with the auxiliary battery.
Several common signs indicate the need for auxiliary battery diagnostics. Addressing these symptoms promptly can prevent further damage and ensure vehicle reliability. According to ASE (National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence) certified technicians, the following symptoms should raise suspicion about the auxiliary battery:
- Start-Stop System Malfunctions: If the start-stop system fails to engage or disengage properly, it could indicate an issue with the auxiliary battery.
- Error Messages on the Dashboard: Warning lights or messages related to the battery or electrical system on the dashboard.
- Electrical Issues: Problems with electronic accessories, such as the infotainment system, navigation, or interior lighting.
- Difficulty Starting the Vehicle: Although less common, a failing auxiliary battery can sometimes contribute to starting issues.
3. Preparing for Diagnostics with DTS Monaco
Proper setup, including hardware and software installation, is crucial for effective diagnostics. A stable power supply is also essential to prevent interruptions during the diagnostic process.
Before diving into the diagnostic process, it’s crucial to ensure that your hardware and software are correctly set up. Quoting industry experts at SEMA (Specialty Equipment Market Association), proper preparation can significantly reduce diagnostic time and prevent errors. Here’s what you need to do:
- Hardware Setup: Connect the diagnostic interface (e.g., MB Star C4/C5/C6) to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and your computer.
- Software Installation: Ensure DTS Monaco is correctly installed and updated with the latest version and relevant database files. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN can help ensure you have the correct setup and databases.
- Vehicle Information: Have the vehicle’s VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) readily available for accurate identification and access to the correct diagnostic protocols.
- Stable Power Supply: Connect a stable power supply to the vehicle to maintain consistent voltage during the diagnostic process, preventing data corruption or ECU damage.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Auxiliary Battery Issues with DTS Monaco
Follow these steps to accurately diagnose auxiliary battery issues, ensuring a systematic and thorough approach.
Diagnosing auxiliary battery issues with DTS Monaco requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
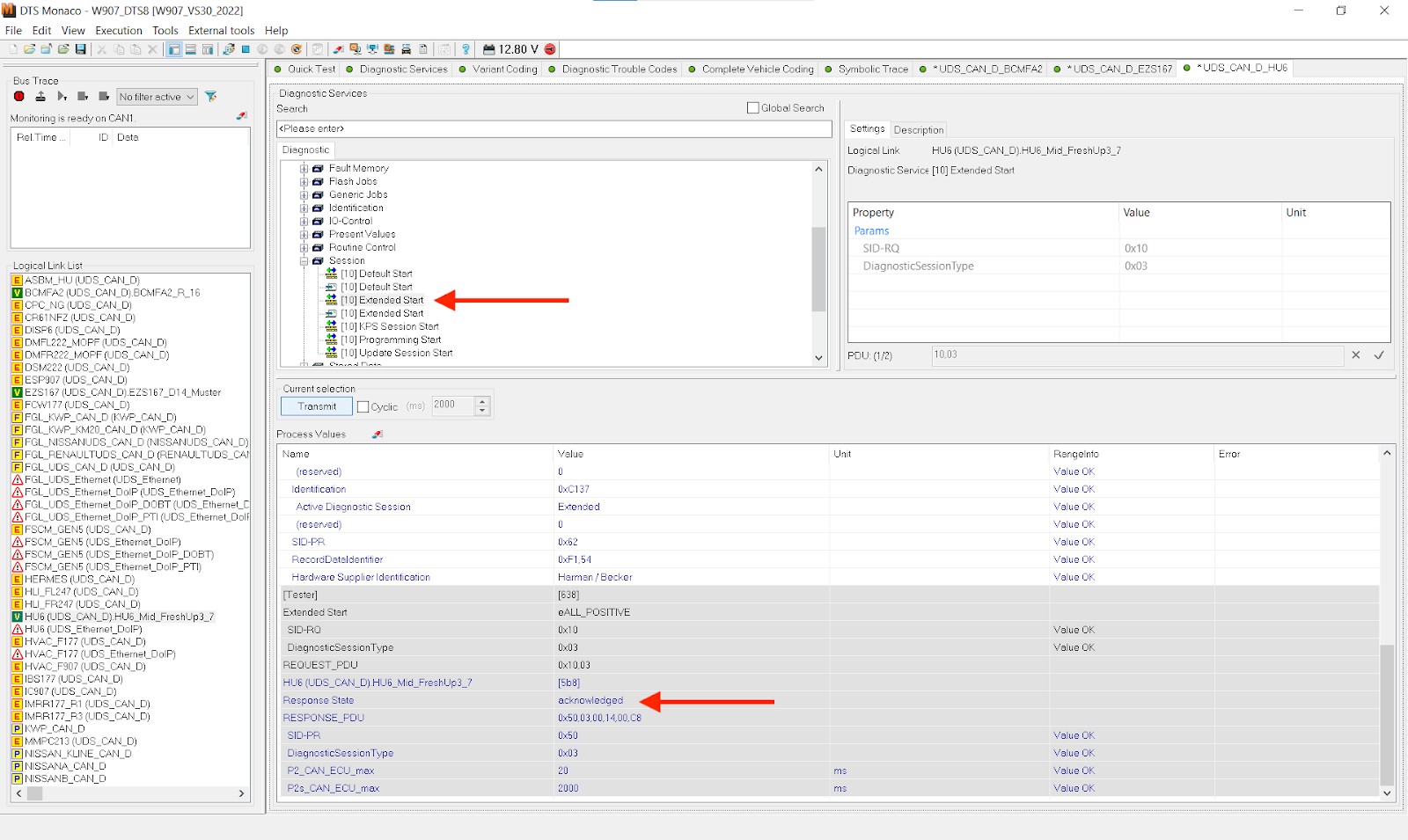
4.1. Connect to the Vehicle
Launch DTS Monaco and establish a connection to the vehicle using the appropriate diagnostic interface.
First, ensure your diagnostic interface (like MB Star C4, C5, or C6) is properly connected to both the vehicle’s OBD-II port and your computer. Open DTS Monaco and select the correct workspace that corresponds to your vehicle model. This workspace contains all the necessary diagnostic data and protocols for your vehicle. Once the workspace is loaded, establish a connection to the vehicle by selecting the appropriate communication interface. Verify that the connection is stable before proceeding.
4.2. Access the Relevant ECU
Navigate to the ECU responsible for managing the auxiliary battery system. This is often the energy management or battery control module.
Once connected, navigate to the list of available ECUs. The ECU responsible for managing the auxiliary battery system may vary depending on the vehicle model but is typically labeled as the “Energy Management Module” or “Battery Control Module.” Select the appropriate ECU to open a new diagnostic session. This step is critical for accessing specific diagnostic information and tests related to the auxiliary battery.
4.3. Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Retrieve and document any DTCs related to the auxiliary battery. Note the code numbers and descriptions for further analysis.
In the selected ECU, go to the “Diagnostic Jobs” or “Fault Memory” section. Here, you can read out any stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to the auxiliary battery system. Record each DTC along with its description, as this information will be essential for diagnosing the issue. Be sure to clear the codes only after documenting them, as they provide valuable insights into the nature and history of the problem.
4.4. Monitor Real-Time Data
Observe real-time data parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature of the auxiliary battery under various conditions.
Navigate to the “Actual Values” or “Live Data” section in DTS Monaco. Here, you can monitor real-time data parameters related to the auxiliary battery. Key parameters to observe include voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge. Monitor these values under different conditions, such as during engine start, idle, and with various electrical loads activated (e.g., headlights, air conditioning). Compare the observed values with the expected ranges to identify any anomalies.
4.5. Perform Guided Tests
Use DTS Monaco’s guided test functions to perform specific diagnostic routines for the auxiliary battery system.
DTS Monaco offers guided test functions that can help you perform specific diagnostic routines for the auxiliary battery system. These tests may include load tests, voltage drop tests, and insulation resistance tests. Access the “Guided Tests” or “Diagnostic Routines” section and select the appropriate test for the auxiliary battery. Follow the on-screen instructions carefully and record the results. These tests provide valuable insights into the battery’s health and performance.
4.6. Analyze the Results
Interpret the DTCs and real-time data to pinpoint the root cause of the auxiliary battery issue.
After gathering all the necessary data, analyze the DTCs, real-time data, and guided test results to pinpoint the root cause of the auxiliary battery issue. Compare the observed values with the expected ranges and consult the vehicle’s service manual for additional information. Common issues may include a faulty battery, a malfunctioning charging system, or a wiring problem.
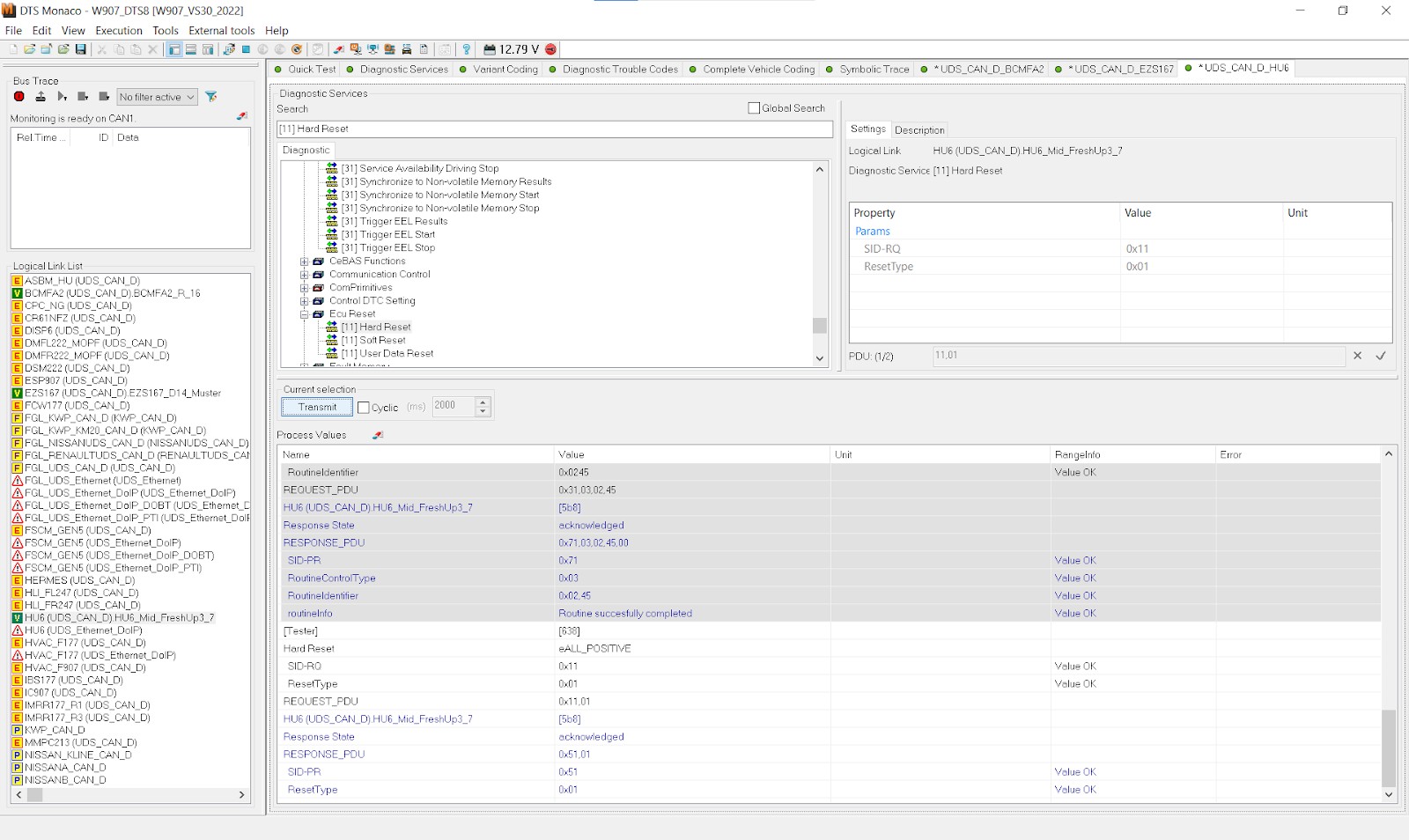
4.7. Verify the Repair
After performing the necessary repairs, use DTS Monaco to clear the DTCs and verify that the auxiliary battery system is functioning correctly.
Once you have performed the necessary repairs, use DTS Monaco to clear the DTCs and verify that the auxiliary battery system is functioning correctly. Monitor the real-time data parameters again to ensure that the voltage, current, and temperature are within the expected ranges. Perform another guided test to confirm that the auxiliary battery system is operating as intended. If any issues persist, re-evaluate the diagnostic data and repeat the repair process as needed.
 Diagnostic Interface Connected to Vehicle OBD-II Port
Diagnostic Interface Connected to Vehicle OBD-II Port
5. Common Diagnostic Scenarios and Solutions
Address frequent issues such as low voltage, charging problems, and faulty battery sensors with targeted solutions.
Here are some common diagnostic scenarios encountered while working with auxiliary batteries and targeted solutions. Drawing insights from training materials at DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN, these scenarios cover frequent issues and practical approaches to resolve them effectively.
5.1. Low Voltage Issues
If the auxiliary battery voltage is consistently low, check the charging system and for parasitic drains.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Check Charging System: Use DTS Monaco to monitor the charging voltage from the alternator. A healthy charging system should provide a voltage between 13.5V and 14.5V.
- Parasitic Drain Test: Perform a parasitic drain test by measuring the current draw when the vehicle is off. Excessive current draw (more than 50mA) indicates a parasitic drain.
- Battery Load Test: Conduct a load test using DTS Monaco to assess the battery’s ability to hold a charge under load. A significant voltage drop during the load test indicates a failing battery.
Solutions:
- Replace Battery: If the battery fails the load test, replace it with a new auxiliary battery that meets the vehicle’s specifications.
- Repair Charging System: If the charging voltage is out of range, diagnose and repair the alternator or voltage regulator.
- Identify and Eliminate Parasitic Drains: Use a multimeter to trace the source of the parasitic drain. Common causes include faulty modules, aftermarket accessories, or wiring issues.
5.2. Charging Problems
Investigate issues preventing the auxiliary battery from charging properly, such as a faulty charging module or wiring problems.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Check Charging Module: Use DTS Monaco to access the charging module and check for DTCs or abnormal readings.
- Wiring Inspection: Inspect the wiring and connections between the charging module, auxiliary battery, and alternator for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Voltage Drop Test: Perform a voltage drop test on the charging circuit to identify excessive resistance.
Solutions:
- Replace Charging Module: If the charging module is faulty, replace it with a new module.
- Repair Wiring: Repair or replace any damaged wiring or connectors in the charging circuit.
- Clean Connections: Clean and tighten any corroded or loose connections to ensure proper electrical contact.
5.3. Faulty Battery Sensors
Address issues related to faulty sensors that provide incorrect data about the battery’s condition.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Check Sensor Data: Use DTS Monaco to monitor the data from the battery sensors, such as voltage, current, and temperature. Compare the readings with the actual values.
- Sensor Diagnostic Codes: Check for DTCs related to the battery sensors.
- Wiring Inspection: Inspect the wiring and connections to the battery sensors for damage or corrosion.
Solutions:
- Replace Faulty Sensors: If the battery sensors are providing incorrect data, replace them with new sensors.
- Repair Wiring: Repair any damaged wiring or connectors to the battery sensors.
- Calibrate Sensors: In some cases, the battery sensors may need to be calibrated after replacement. Use DTS Monaco to perform the calibration procedure.
5.4. Start-Stop System Issues
Diagnose problems with the start-stop system by monitoring the auxiliary battery’s performance during engine start and stop cycles.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Monitor Battery Voltage: Use DTS Monaco to monitor the auxiliary battery voltage during start-stop cycles. A significant voltage drop indicates a problem with the battery or charging system.
- Check Start-Stop System Codes: Check for DTCs related to the start-stop system.
- Test Start-Stop Functionality: Perform a start-stop system test using DTS Monaco to evaluate the system’s performance.
Solutions:
- Replace Battery: If the auxiliary battery voltage drops excessively during start-stop cycles, replace it with a new battery.
- Repair Charging System: If the charging system is not providing sufficient voltage, diagnose and repair the alternator or voltage regulator.
- Address Start-Stop System Codes: Diagnose and repair any issues related to the start-stop system based on the DTCs.
5.5. Communication Errors
Troubleshoot communication errors between the auxiliary battery system and other vehicle modules.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Check Communication Codes: Check for DTCs related to communication errors between the auxiliary battery system and other vehicle modules.
- CAN Bus Test: Perform a CAN (Controller Area Network) bus test using DTS Monaco to check the integrity of the communication network.
- Wiring Inspection: Inspect the wiring and connections between the auxiliary battery system and other modules for damage or corrosion.
Solutions:
- Repair Wiring: Repair any damaged wiring or connectors in the communication network.
- Update Software: Update the software of the affected modules to ensure compatibility.
- Replace Modules: If a module is faulty and causing communication errors, replace it with a new module.
By addressing these common diagnostic scenarios with targeted solutions, automotive technicians can effectively troubleshoot and repair auxiliary battery issues, ensuring the reliable operation of modern vehicles. The key is to use DTS Monaco effectively, which DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN can help you with.
 DTS Monaco Software Interface
DTS Monaco Software Interface
6. Advanced Techniques for Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics
Explore advanced techniques like component testing and circuit analysis to address complex issues beyond standard diagnostics.
Delving into advanced diagnostic techniques is crucial for tackling intricate issues that extend beyond the scope of standard procedures. Citing automotive engineering experts at Bosch, advanced diagnostics involve component testing and circuit analysis, which can uncover hidden problems. These techniques enable technicians to thoroughly evaluate the system’s functionality, ensuring accurate and effective repairs.
6.1. Component Testing
Perform individual component tests to verify the functionality of sensors, relays, and modules within the auxiliary battery system.
Component testing involves assessing individual parts of the auxiliary battery system to ensure they meet performance specifications. This technique is essential for identifying faulty components that may not be apparent through standard diagnostic procedures. Here’s how to perform component testing effectively:
- Sensors: Use DTS Monaco to monitor sensor outputs (voltage, current, temperature) and compare them to expected values. For example, a temperature sensor should provide readings that correlate with the actual battery temperature. Discrepancies indicate a faulty sensor.
- Relays: Test relays by checking their continuity and activation using a multimeter. Ensure that the relay switches properly when energized and that there is no excessive resistance in the circuit.
- Modules: Evaluate modules by checking their input and output signals using DTS Monaco. Verify that the module responds correctly to commands and that its internal diagnostics do not indicate any faults.
6.2. Circuit Analysis
Conduct detailed circuit analysis to identify wiring issues, shorts, and open circuits that can affect the auxiliary battery system.
Circuit analysis involves examining the electrical pathways within the auxiliary battery system to identify faults such as shorts, open circuits, and high resistance connections. This technique is crucial for diagnosing intermittent issues and ensuring the integrity of the electrical system. Here’s how to perform circuit analysis effectively:
- Voltage Drop Testing: Measure the voltage drop across various points in the circuit while the system is under load. Excessive voltage drop indicates high resistance due to corroded connections, damaged wiring, or faulty components.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of wires and connections. An open circuit indicates a broken wire or a disconnected connector.
- Insulation Testing: Perform insulation testing to check for shorts to ground. Use an insulation tester (megohmmeter) to apply a high voltage and measure the insulation resistance. Low resistance indicates a short circuit.
6.3. Analyzing Wiring Diagrams
Utilize wiring diagrams to understand the connections and relationships between various components in the auxiliary battery system.
Wiring diagrams are essential tools for understanding the layout and connections of the auxiliary battery system. By analyzing wiring diagrams, technicians can trace circuits, identify components, and locate potential fault areas. Here’s how to effectively use wiring diagrams in diagnostics:
- Understanding Symbols and Conventions: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used in wiring diagrams, such as component symbols, wire colors, and connector designations.
- Tracing Circuits: Use the wiring diagram to trace the circuits related to the auxiliary battery system. Follow the wires from the power source to the components and back to ground to understand the flow of electricity.
- Identifying Components: Locate the components in the wiring diagram and identify their functions and connections. This helps you understand how the components interact with each other and the rest of the system.
- Locating Connectors and Splices: Use the wiring diagram to locate connectors and splices in the wiring harness. These are common areas for corrosion and wiring damage.
6.4. Using Oscilloscopes
Employ oscilloscopes to visualize electrical signals and diagnose intermittent issues or signal abnormalities in the auxiliary battery system.
Oscilloscopes are powerful tools for visualizing electrical signals and diagnosing intermittent issues or signal abnormalities in the auxiliary battery system. By displaying the voltage and current waveforms, oscilloscopes can help technicians identify problems that are not apparent through standard diagnostic procedures. Here’s how to use oscilloscopes effectively:
- Setting Up the Oscilloscope: Connect the oscilloscope to the circuit under test and adjust the settings to display the voltage and current waveforms.
- Analyzing Waveforms: Analyze the waveforms for abnormalities such as signal clipping, noise, or distortion. These abnormalities can indicate problems with the components or wiring in the circuit.
- Capturing Intermittent Signals: Use the oscilloscope’s trigger function to capture intermittent signals that occur sporadically. This helps you diagnose problems that are difficult to reproduce.
By mastering these advanced techniques, automotive technicians can effectively diagnose and repair complex issues in the auxiliary battery system, ensuring the reliable operation of modern vehicles. Training resources and hands-on courses at DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN can help you acquire these skills and stay ahead in the field of automotive diagnostics.
 Example of a wiring diagram for a vehicle's electrical system
Example of a wiring diagram for a vehicle's electrical system
7. Best Practices for Maintaining Auxiliary Batteries
Implement preventive measures to prolong the life of auxiliary batteries and ensure reliable vehicle operation.
Adopting proactive maintenance strategies can significantly extend the lifespan of auxiliary batteries and ensure dependable vehicle performance. According to insights shared by automotive maintenance experts at AAA (American Automobile Association), implementing these best practices can prevent unexpected failures and optimize battery health.
7.1. Regular Voltage Checks
Periodically check the auxiliary battery voltage to identify potential issues early on. A healthy battery should maintain a voltage between 12.6V and 12.8V when fully charged.
Regularly checking the voltage of the auxiliary battery is a simple yet effective way to monitor its condition. A healthy battery should maintain a voltage between 12.6V and 12.8V when fully charged. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals. Here are the steps to perform a voltage check:
- Gather Your Tools: You will need a multimeter, safety glasses, and gloves.
- Prepare the Vehicle: Turn off the vehicle and open the hood to access the auxiliary battery.
- Set Up the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to DC voltage mode and select a range that can measure up to 20V.
- Connect the Multimeter: Connect the red lead of the multimeter to the positive (+) terminal of the battery and the black lead to the negative (-) terminal.
- Read the Voltage: Read the voltage displayed on the multimeter. A fully charged battery should read between 12.6V and 12.8V.
7.2. Proper Charging Habits
Avoid deep discharges by ensuring the vehicle’s charging system is functioning correctly. Regularly check the charging voltage and address any issues promptly.
Proper charging habits are essential for maintaining the health of the auxiliary battery. Avoid deep discharges by ensuring that the vehicle’s charging system is functioning correctly. Regularly check the charging voltage and address any issues promptly. Here are some tips for proper charging habits:
- Check Charging Voltage: Use DTS Monaco to monitor the charging voltage from the alternator. A healthy charging system should provide a voltage between 13.5V and 14.5V.
- Avoid Excessive Electrical Load: Minimize the use of electrical accessories when the engine is off to prevent deep discharges.
- Use a Battery Maintainer: If the vehicle is not used for extended periods, use a battery maintainer to keep the auxiliary battery fully charged.
7.3. Clean Battery Terminals
Keep the battery terminals clean and free of corrosion to ensure a good electrical connection. Use a battery terminal cleaner and a wire brush to remove any buildup.
Corrosion on the battery terminals can impede the flow of electricity and lead to charging problems. Keep the battery terminals clean and free of corrosion to ensure a good electrical connection. Use a battery terminal cleaner and a wire brush to remove any buildup. Here’s how to clean the battery terminals:
- Gather Your Supplies: You will need a battery terminal cleaner, a wire brush, safety glasses, gloves, and a wrench.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative (-) terminal first, followed by the positive (+) terminal.
- Clean the Terminals: Use the wire brush to scrub the terminals and remove any corrosion.
- Apply Battery Terminal Cleaner: Apply battery terminal cleaner to the terminals to neutralize any remaining acid.
- Reassemble the Terminals: Reconnect the positive (+) terminal first, followed by the negative (-) terminal.
- Apply Terminal Protectant: Apply a terminal protectant to prevent future corrosion.
7.4. Regular Load Tests
Perform load tests to assess the battery’s ability to deliver power under load. This helps identify weak batteries before they fail completely.
Regular load tests can help assess the battery’s ability to deliver power under load. This helps identify weak batteries before they fail completely. Use DTS Monaco to perform a load test on the auxiliary battery. Here’s how to perform a load test:
- Connect the Load Tester: Connect the load tester to the battery terminals, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Apply the Load: Apply the specified load to the battery for the recommended duration.
- Monitor the Voltage: Monitor the battery voltage during the load test. A significant voltage drop indicates a weak battery.
- Interpret the Results: Compare the test results to the battery’s specifications to determine its condition.
7.5. Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Protect the auxiliary battery from extreme temperatures, as heat and cold can accelerate battery degradation. Park the vehicle in a shaded area or use a battery thermal blanket in cold climates.
Extreme temperatures can accelerate battery degradation. Protect the auxiliary battery from extreme temperatures by parking the vehicle in a shaded area or using a battery thermal blanket in cold climates. Here are some tips for protecting the battery from extreme temperatures:
- Park in the Shade: Park the vehicle in a shaded area during hot weather to prevent the battery from overheating.
- Use a Battery Thermal Blanket: Use a battery thermal blanket in cold climates to insulate the battery and prevent it from freezing.
- Avoid Prolonged Exposure: Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures, such as leaving the vehicle parked in direct sunlight for extended periods.
By following these best practices, automotive technicians and vehicle owners can prolong the life of auxiliary batteries and ensure reliable vehicle operation. Regular maintenance and proactive measures can prevent unexpected failures and optimize battery health, ensuring that modern vehicles perform at their best. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers resources and training to help you implement these practices effectively.
 Auxiliary Battery in a Vehicle
Auxiliary Battery in a Vehicle
8. Car Coding and Auxiliary Battery Systems
Understand how car coding with DTS Monaco can optimize auxiliary battery functions and improve vehicle performance.
Car coding with DTS Monaco offers a way to fine-tune auxiliary battery functions and enhance overall vehicle performance. Automotive customization experts at Carista emphasize that coding can unlock hidden features and optimize system parameters, leading to improved efficiency and reliability.
8.1. Enabling and Disabling Features
Use DTS Monaco to enable or disable features related to the auxiliary battery, such as start-stop functionality or battery monitoring systems.
Car coding allows technicians to customize various features related to the auxiliary battery system. Using DTS Monaco, you can enable or disable features such as start-stop functionality or battery monitoring systems. Here are some examples:
- Start-Stop Functionality: You can disable the start-stop system if it is causing issues or if the driver prefers it to be off.
- Battery Monitoring Systems: You can enable or disable battery monitoring systems that track the battery’s health and performance.
- Power Management Settings: You can adjust power management settings to optimize the use of the auxiliary battery.
8.2. Adjusting System Parameters
Modify system parameters to optimize the performance of the auxiliary battery, such as charging voltage or discharge rates.
Car coding can also be used to adjust system parameters that affect the performance of the auxiliary battery. Using DTS Monaco, you can modify parameters such as charging voltage or discharge rates to optimize the battery’s performance. Here are some examples:
- Charging Voltage: You can adjust the charging voltage to ensure that the auxiliary battery is properly charged.
- Discharge Rates: You can modify the discharge rates to prevent the battery from being excessively discharged.
- Power Distribution: You can customize the power distribution to prioritize certain systems or accessories.
8.3. Recoding After Replacement
Recode the vehicle’s ECU after replacing the auxiliary battery to ensure proper integration and function.
When replacing the auxiliary battery, it is often necessary to recode the vehicle’s ECU to ensure proper integration and function. This is particularly important for vehicles with advanced battery management systems. Using DTS Monaco, you can perform the recoding procedure to ensure that the new battery is properly recognized and managed by the vehicle’s systems. Here are the steps to recode the ECU after replacing the auxiliary battery:
- Connect to the Vehicle: Connect DTS Monaco to the vehicle using the appropriate diagnostic interface.
- Access the Battery Management Module: Navigate to the battery management module in DTS Monaco.
- Select the Recoding Function: Select the recoding function or battery replacement function in DTS Monaco.
- Follow the On-Screen Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the recoding procedure.
- Verify the Recoding: Verify that the recoding was successful by checking the battery’s status and performance using DTS Monaco.
8.4. Customizing Power Management
Customize the vehicle’s power management settings to optimize the use of the auxiliary battery and improve overall efficiency.
Car coding allows technicians to customize the vehicle’s power management settings to optimize the use of the auxiliary battery and improve overall efficiency. Using DTS Monaco, you can adjust settings such as the priority of electrical systems, the timing of power distribution, and the threshold for low-power mode. Here are some examples:
- Priority of Electrical Systems: You can prioritize certain electrical systems, such as the infotainment system or climate control, to ensure that they receive adequate power.
- Timing of Power Distribution: You can adjust the timing of power distribution to optimize the use of the auxiliary battery.
- Threshold for Low-Power Mode: You can adjust the threshold for low-power mode to prevent the battery from being excessively discharged.
By leveraging car coding techniques with DTS Monaco, automotive technicians can optimize auxiliary battery functions, improve vehicle performance, and enhance the overall driving experience. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training and resources to help you master these techniques and stay ahead in the field of automotive diagnostics and customization.
 DTS Monaco Car Coding Interface
DTS Monaco Car Coding Interface
9. Safety Precautions During Auxiliary Battery Diagnostics
Prioritize safety by following these precautions during the diagnostic process to prevent injuries and damage to the vehicle.
Ensuring safety during auxiliary battery diagnostics is paramount to prevent injuries and vehicle damage. Drawing on guidelines from OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), adhering to these safety precautions ensures a secure working environment.
9.1. Wear Protective Gear
Always wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from battery acid and electrical hazards.
Always wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from battery acid and electrical hazards. Battery acid is corrosive and can cause severe burns if it comes into contact with your skin or eyes. Electrical hazards, such as short circuits, can cause burns or electric shock. Here’s how to properly wear protective gear:
- Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses that meet ANSI Z87.1 standards to protect your eyes from battery acid and debris.
- Gloves: Wear chemical-resistant gloves to protect your hands from battery acid and electrical hazards.
9.2. Disconnect the Battery Properly
Disconnect the negative terminal first to avoid short circuits. Ensure the ignition is off and the keys are removed.
Disconnecting the battery properly is essential to avoid short circuits and damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. Always disconnect the negative terminal first to prevent the possibility of a short circuit. Ensure that the ignition is off and the keys are removed before disconnecting the battery. Here are the steps to disconnect the battery properly:
- Gather Your Tools: You will need a wrench and safety glasses.
- Locate the Battery: Locate the auxiliary battery in the vehicle.
- Disconnect the Negative Terminal: Use the wrench to loosen the nut on the negative (-) terminal and disconnect the cable.
- Disconnect the Positive Terminal: Use the wrench to loosen the nut on the positive (+) terminal and disconnect the cable.
- Secure the Cables: Secure the cables away from the battery to prevent them from accidentally coming into contact with the terminals.
9.3. Work in a Well-Ventilated Area
Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful gases emitted by the battery during charging or testing.
Working in a well-ventilated area is essential to avoid inhaling harmful gases emitted by the battery during charging or testing. Batteries can emit hydrogen gas, which is flammable and can cause explosions if it accumulates in a confined space. Here are some tips for working in a well-ventilated area:
- Open Doors and Windows: Open doors and windows to allow fresh air to circulate.
- Use a Fan: Use a fan to circulate the air and remove any harmful gases.
- Avoid Confined Spaces: Avoid working in confined spaces where gases can accumulate.
9.4. Use Insulated Tools
Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks when working near live circuits.
Using insulated tools is essential to prevent electrical shocks when working near live circuits. Insulated tools have a non-conductive coating that protects you from coming into contact with electricity. Here are some tips for using insulated tools:
- Inspect Tools: Inspect the tools before each use to ensure that the insulation is not damaged.
- Use Properly Rated Tools: Use tools that are properly rated for the voltage of the circuit you are working on.
- Avoid Contact with Metal: Avoid contact with metal parts of the tools when working near live circuits.
9.5. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety procedures when working with auxiliary batteries and DTS Monaco.
Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety procedures when working with auxiliary batteries and DTS Monaco. The manufacturer’s guidelines provide specific instructions for diagnosing and repairing the auxiliary battery system, as well as safety precautions to follow. Here are some tips for following manufacturer guidelines:
- Read the Manual: Read the manufacturer’s manual before starting any diagnostic or repair work.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the instructions in the manual carefully.
- Use Recommended Tools: Use the recommended tools and equipment for the job.
- Ask for Help: If you are unsure about any step, ask for help from a qualified technician.
By following these safety precautions, automotive technicians can minimize the risk of injuries and damage to the vehicle during auxiliary battery diagnostics. Adhering to safety protocols ensures a safe and efficient working environment, promoting reliable and effective repairs. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN emphasizes the importance of safety in all training materials and courses.
 Technician Wearing Safety Gear
Technician Wearing Safety Gear
10. Where to Find Training and Resources for DTS Monaco
Enhance your skills with training courses and resources available for