How does DTS Monaco handle manufacturer sub-codes or failure type bytes associated with DTCs? DTS Monaco displays them if available, offering crucial insights for precise automotive diagnostics and car coding, a key aspect covered in detail at DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN. Learning to interpret these codes can significantly improve your diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Dive in to explore the comprehensive capabilities of DTS Monaco and elevate your car coding skills with advanced training in this specialized area.
Contents
- 1. What are Manufacturer Sub-Codes or Failure Type Bytes in DTCs?
- 2. How Does DTS Monaco Display Sub-Codes?
- 3. Why Are Manufacturer Sub-Codes Important?
- 4. Where Can You Learn More About DTS Monaco and DTC Sub-Codes?
- 5. What Are the Benefits of Learning from DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN?
- 6. What Tools and Equipment Do You Need?
- 7. How Does DTS Monaco Enhance Diagnostic Accuracy?
- 8. What Are Some Common DTC Sub-Code Examples?
- 9. How Can You Stay Updated on the Latest DTS Monaco Features?
- 10. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Using DTS Monaco?
- 11. What is Car Coding and Why is it Important?
- 12. What is the Role of J2534 Pass-Thru Devices in Car Coding?
- 13. How to Choose the Right J2534 Pass-Thru Device?
- 14. What are CBF and SMR-D Files in DTS Monaco?
- 15. How Do Seed Key Calculators Work in Car Coding?
- 16. How to Use DTS Monaco to Read and Clear DTCs?
- 17. What are the Risks Associated with Car Coding?
- 18. Can DTS Monaco be Used for ECU Flashing?
- 19. How to Backup and Restore ECU Data with DTS Monaco?
- 20. What are the Best Practices for Car Coding with DTS Monaco?
- FAQ Section
1. What are Manufacturer Sub-Codes or Failure Type Bytes in DTCs?
Manufacturer sub-codes, also known as failure type bytes, are additional pieces of information that accompany Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These sub-codes provide a more granular description of the fault, offering specific details about the conditions or circumstances under which the DTC was triggered. For instance, a DTC might indicate a general sensor fault, while the sub-code specifies whether the sensor signal is too high, too low, intermittent, or out of range.
Understanding these sub-codes is crucial for pinpointing the root cause of a problem, reducing diagnostic time, and performing accurate repairs. In the context of car coding and advanced diagnostics, having access to this level of detail can make a significant difference in the effectiveness and efficiency of your work.
2. How Does DTS Monaco Display Sub-Codes?
DTS Monaco is designed to display manufacturer sub-codes or failure type bytes associated with DTCs, provided that the information is available in the vehicle’s diagnostic data. When you use DTS Monaco to read DTCs from a vehicle’s control units, the software will present any accompanying sub-codes alongside the main DTC.
The way DTS Monaco displays these sub-codes can vary depending on the specific vehicle and control unit. Typically, the sub-codes are shown as hexadecimal or decimal values, often with a brief description or abbreviation to indicate their meaning. Some manufacturers use standardized sub-code formats, while others have proprietary codes specific to their vehicles.
Example:
Let’s say a DTC like “P0101 – Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem” is displayed. DTS Monaco might also show a sub-code like “0x21,” which could indicate that the signal is erratic or intermittent. Understanding this sub-code helps you focus your diagnostic efforts on potential wiring issues or loose connections rather than a complete sensor failure.
3. Why Are Manufacturer Sub-Codes Important?
Manufacturer sub-codes are important because they offer a deeper layer of diagnostic information beyond the standard DTC. This additional information can help technicians and car coding specialists:
- Pinpoint the exact nature of the fault: Sub-codes provide more specific details about the fault, such as whether it is related to a high or low signal, an open circuit, a short to ground, or other specific conditions.
- Reduce diagnostic time: By providing more precise information, sub-codes can help technicians quickly identify the root cause of a problem, reducing the need for extensive troubleshooting.
- Improve repair accuracy: With a better understanding of the fault, technicians can perform more accurate and effective repairs, reducing the likelihood of repeat issues.
- Perform advanced car coding: Sub-codes can sometimes provide insights into the parameters that need to be adjusted during car coding procedures, ensuring that the modifications are appropriate for the specific vehicle and its configuration.
4. Where Can You Learn More About DTS Monaco and DTC Sub-Codes?
To gain in-depth knowledge about DTS Monaco and how it handles DTC sub-codes, DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers extensive resources and training programs. Our courses are designed to equip you with the skills needed to effectively use DTS Monaco for advanced diagnostics and car coding.
By joining our training programs, you’ll learn how to:
- Navigate the DTS Monaco interface and access diagnostic data.
- Interpret DTCs and their associated sub-codes.
- Use sub-codes to pinpoint the root cause of automotive faults.
- Perform advanced car coding procedures with confidence.
We provide step-by-step guidance, practical examples, and hands-on exercises to ensure you can confidently apply your new skills in real-world scenarios.
5. What Are the Benefits of Learning from DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN?
Learning about DTS Monaco from DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers several key benefits:
- Expert Instruction: Our courses are taught by experienced professionals with extensive knowledge of DTS Monaco and automotive diagnostics.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: We cover all aspects of DTS Monaco, from basic operation to advanced car coding techniques.
- Hands-On Training: Our programs include practical exercises that allow you to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios.
- Up-to-Date Information: We keep our curriculum current with the latest developments in automotive technology and diagnostic tools.
- Career Advancement: Mastering DTS Monaco can enhance your skills and open doors to new career opportunities in the automotive industry.
6. What Tools and Equipment Do You Need?
To effectively use DTS Monaco and interpret DTC sub-codes, you will need the following tools and equipment:
- DTS Monaco Software: The core software for accessing and analyzing vehicle diagnostic data.
- J2534 Pass-Thru Device: An interface device that connects your computer to the vehicle’s OBD-II port, allowing communication with the vehicle’s control units.
- Laptop: A Windows-based laptop with sufficient processing power and storage space to run DTS Monaco and related software.
- Vehicle Diagnostic Manuals: Vehicle-specific diagnostic manuals that provide detailed information about DTCs, sub-codes, and troubleshooting procedures.
Having the right tools and resources is essential for accurate diagnostics and effective car coding.
7. How Does DTS Monaco Enhance Diagnostic Accuracy?
DTS Monaco enhances diagnostic accuracy by providing a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s diagnostic data, including DTCs, sub-codes, and real-time sensor readings. By integrating this information, technicians can:
- Identify subtle issues: Sub-codes often reveal subtle issues that would be missed by simply reading the main DTC.
- Correlate data: DTS Monaco allows you to correlate DTCs with real-time sensor data to identify the conditions that trigger specific faults.
- Perform targeted tests: With a clearer understanding of the fault, you can perform targeted tests to confirm the diagnosis and avoid unnecessary repairs.
- Reduce errors: By providing more precise information, DTS Monaco reduces the likelihood of misdiagnosis and incorrect repairs.
8. What Are Some Common DTC Sub-Code Examples?
DTC sub-codes vary depending on the vehicle manufacturer and the specific control unit. However, some common examples include:
| Sub-Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| 0x11 | Short to Ground | Damaged wiring, shorted sensor, faulty control unit |
| 0x12 | Short to Positive | Damaged wiring, shorted sensor, faulty control unit |
| 0x13 | Open Circuit | Broken wiring, disconnected sensor, faulty control unit |
| 0x21 | Signal Above Maximum Threshold | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, incorrect calibration |
| 0x22 | Signal Below Minimum Threshold | Faulty sensor, wiring issue, incorrect calibration |
| 0x29 | Signal Invalid | Corrupted data, sensor malfunction, communication error |
| 0x41 | Signal Intermittent/Erratic | Loose connection, wiring issue, faulty sensor |
| 0x81 | Data Plausibility Failure | Mismatched data from different sensors, incorrect calibration, faulty control unit |
| 0xF1 | Component Failure | Faulty sensor, internal component failure |
| 0xF2 | Mechanical Failure | Physical damage, obstruction, binding component |
These sub-codes offer valuable insights into the nature of the fault, helping technicians quickly identify the root cause of the problem.
9. How Can You Stay Updated on the Latest DTS Monaco Features?
Staying updated on the latest DTS Monaco features is crucial for maximizing your diagnostic and car coding capabilities. Here are some effective strategies:
- Follow DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN: We regularly publish articles, tutorials, and training materials on the latest DTS Monaco features and updates.
- Attend Industry Conferences: Automotive industry conferences often include presentations and workshops on advanced diagnostic tools like DTS Monaco.
- Join Online Forums: Online forums and communities dedicated to automotive diagnostics and car coding are great places to share information and learn from other professionals.
- Subscribe to Newsletters: Subscribe to newsletters from automotive technology providers to receive updates on new products and features.
- Participate in Training Programs: Enroll in advanced training programs to gain hands-on experience with the latest DTS Monaco features.
10. What Are the Ethical Considerations When Using DTS Monaco?
When using DTS Monaco for car coding and diagnostics, it’s essential to consider the ethical implications of your work. Here are some key considerations:
- Transparency: Always inform vehicle owners about any modifications or adjustments you make to their vehicle’s software.
- Compliance: Ensure that your car coding activities comply with all applicable laws and regulations, including emissions standards and safety requirements.
- Data Privacy: Respect the privacy of vehicle owners by protecting their personal data and avoiding unauthorized access to vehicle systems.
- Professionalism: Conduct your work with integrity and professionalism, adhering to industry best practices and ethical standards.
By considering these ethical considerations, you can ensure that your use of DTS Monaco is both effective and responsible.
11. What is Car Coding and Why is it Important?
Car coding refers to the process of modifying a vehicle’s software to enable or disable certain features, adjust performance parameters, or customize vehicle behavior. This can involve changing settings in various control units (ECUs) to tailor the vehicle to specific preferences or requirements.
Car coding is important for several reasons:
- Customization: Allows vehicle owners to personalize their vehicle’s features and behavior to match their preferences.
- Retrofitting: Enables the addition of new features or components to a vehicle that were not originally installed at the factory.
- Performance Tuning: Adjusts engine and transmission parameters to improve performance, fuel efficiency, or throttle response.
- Repair and Maintenance: Corrects software glitches or resets systems after repairs or component replacements.
- Enabling Hidden Features: Activates dormant features that are already present in the vehicle’s software but were disabled by the manufacturer.
Understanding car coding is an essential skill for modern automotive technicians, as it allows them to provide a higher level of service and meet the evolving needs of vehicle owners.
12. What is the Role of J2534 Pass-Thru Devices in Car Coding?
J2534 Pass-Thru devices are essential tools for car coding and advanced diagnostics. These devices serve as a communication interface between a computer and a vehicle’s onboard systems, allowing technicians to read and write data to various control units (ECUs).
The key roles of J2534 Pass-Thru devices include:
- Communication Interface: Establishes a connection between the computer and the vehicle’s OBD-II port, enabling data exchange between the two.
- Data Transfer: Allows for the transfer of diagnostic data, software updates, and coding parameters to and from the vehicle’s ECUs.
- Protocol Support: Supports various communication protocols used by different vehicle manufacturers, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of vehicles.
- Standardization: Adheres to the J2534 standard, ensuring interoperability with different diagnostic software and vehicle systems.
Without a J2534 Pass-Thru device, it would be impossible to perform car coding or advanced diagnostics on modern vehicles, as these tasks require direct communication with the vehicle’s ECUs.
13. How to Choose the Right J2534 Pass-Thru Device?
Choosing the right J2534 Pass-Thru device is crucial for successful car coding and diagnostics. Here are some factors to consider:
- Compatibility: Ensure the device is compatible with the vehicles you plan to work on, including the communication protocols and vehicle systems supported.
- Performance: Look for a device with fast data transfer speeds and reliable performance to minimize coding and diagnostic time.
- Software Support: Check if the device is supported by the diagnostic software you intend to use, such as DTS Monaco.
- Reliability: Choose a device from a reputable manufacturer with a track record of producing reliable and durable products.
- Price: Consider your budget and compare the features and performance of different devices to find the best value for your money.
- Updates and Support: Ensure the manufacturer provides regular software updates and technical support to keep the device up-to-date and resolve any issues that may arise.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a J2534 Pass-Thru device that meets your needs and provides reliable performance for your car coding and diagnostic activities.
14. What are CBF and SMR-D Files in DTS Monaco?
CBF (Common Base Format) and SMR-D (Software Module Record – Data) files are essential components in DTS Monaco, providing the necessary data and instructions for communicating with and coding vehicle control units.
- CBF Files: These files contain the communication protocols, diagnostic routines, and coding parameters specific to a particular control unit. They define how DTS Monaco interacts with the ECU, allowing it to read diagnostic data, perform coding operations, and execute diagnostic tests.
- SMR-D Files: These files contain the actual data used for coding and configuration. They provide the specific values and settings that can be modified to customize the vehicle’s features and behavior.
Together, CBF and SMR-D files enable DTS Monaco to perform a wide range of functions, from basic diagnostics to advanced car coding, making them essential resources for automotive technicians and car coding specialists.
15. How Do Seed Key Calculators Work in Car Coding?
Seed key calculators play a critical role in car coding by providing the necessary security access to modify protected control units. Many modern vehicles employ security measures to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive coding parameters, requiring a specific “key” to unlock the ECU before coding can be performed.
Here’s how seed key calculators work:
- Request a Seed: The diagnostic tool (e.g., DTS Monaco) sends a request to the ECU for a “seed” value.
- ECU Provides Seed: The ECU responds with a unique seed value.
- Seed Key Calculator: The seed value is entered into a seed key calculator, which uses a proprietary algorithm to generate a corresponding “key.”
- Send the Key: The generated key is sent back to the ECU.
- ECU Validation: The ECU validates the key against its internal algorithm. If the key is correct, the ECU unlocks and allows coding modifications.
Seed key calculators are essential for accessing and modifying protected control units, enabling technicians to perform advanced car coding tasks that would otherwise be impossible.
16. How to Use DTS Monaco to Read and Clear DTCs?
Using DTS Monaco to read and clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) is a fundamental diagnostic procedure. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Connect to Vehicle: Connect your J2534 Pass-Thru device to the vehicle’s OBD-II port and your computer.
- Launch DTS Monaco: Open the DTS Monaco software on your computer.
- Select Workspace: Choose the appropriate workspace for the vehicle you are working on.
- Connect to ECU: Select the control unit (ECU) you want to diagnose from the list of available ECUs.
- Read DTCs: Navigate to the “Read DTCs” or “Fault Memory” function within DTS Monaco.
- View DTCs: DTS Monaco will display a list of any stored DTCs, along with their descriptions and sub-codes (if available).
- Clear DTCs: To clear the DTCs, select the “Clear DTCs” or “Erase Fault Memory” function.
- Verify: After clearing the DTCs, re-read the fault memory to ensure that the codes have been successfully cleared.
Regularly reading and clearing DTCs is an essential part of automotive maintenance and diagnostics, helping technicians identify and resolve issues before they escalate into major problems.
17. What are the Risks Associated with Car Coding?
While car coding offers many benefits, it also carries certain risks that technicians and vehicle owners should be aware of:
- Software Corruption: Incorrect coding can corrupt the vehicle’s software, leading to malfunctions or system failures.
- Warranty Issues: Unauthorized coding modifications can void the vehicle’s warranty, leaving the owner responsible for repair costs.
- Safety Concerns: Incorrect coding can compromise the vehicle’s safety systems, such as ABS or airbags, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Legal Compliance: Coding modifications that violate emissions standards or safety regulations can result in fines or legal penalties.
- Compatibility Issues: Coding changes that are not compatible with the vehicle’s hardware or other software components can cause conflicts and malfunctions.
To mitigate these risks, it’s essential to have thorough knowledge of the vehicle’s systems and coding procedures, use reliable diagnostic tools and software, and always back up the original coding parameters before making any changes.
18. Can DTS Monaco be Used for ECU Flashing?
Yes, DTS Monaco can be used for ECU flashing, which involves overwriting the existing software on a control unit with a new version. ECU flashing is commonly performed to update software, improve performance, or fix software bugs.
To perform ECU flashing with DTS Monaco, you will need:
- DTS Monaco Software: The core software for accessing and flashing ECU data.
- J2534 Pass-Thru Device: An interface device that connects your computer to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- ECU Flash Files: The correct flash files for the specific ECU and vehicle model.
- Stable Power Supply: A stable power supply to maintain consistent voltage during the flashing process.
ECU flashing is a complex procedure that requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the vehicle’s systems. Incorrect flashing can damage the ECU, so it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use reliable flash files.
19. How to Backup and Restore ECU Data with DTS Monaco?
Backing up and restoring ECU data is a crucial step before performing any car coding or ECU flashing procedures. This allows you to revert to the original settings if something goes wrong during the modification process.
Here’s how to backup and restore ECU data with DTS Monaco:
- Connect to ECU: Connect to the ECU you want to backup using DTS Monaco.
- Read ECU Configuration: Use the “Read ECU Configuration” or similar function to read the current coding parameters from the ECU.
- Save Backup File: Save the read configuration data to a backup file on your computer. Be sure to label the file clearly with the date, time, and ECU name.
- Perform Coding/Flashing: Proceed with your car coding or ECU flashing procedures.
- Restore if Needed: If something goes wrong, connect to the ECU again and use the “Restore ECU Configuration” or similar function to load the backup file and revert to the original settings.
Regularly backing up ECU data can save you from costly mistakes and ensure that you can always restore the vehicle to its original condition if necessary.
20. What are the Best Practices for Car Coding with DTS Monaco?
Following best practices is essential for safe and effective car coding with DTS Monaco. Here are some key recommendations:
- Research: Thoroughly research the coding parameters you plan to modify, ensuring that you understand their function and potential impact on the vehicle.
- Backup: Always backup the original ECU data before making any changes.
- Stable Power: Use a stable power supply to maintain consistent voltage during coding and flashing procedures.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions and coding procedures.
- Verify Compatibility: Ensure that any coding changes are compatible with the vehicle’s hardware and other software components.
- Test Thoroughly: After making coding changes, thoroughly test the affected systems to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Document Changes: Keep a detailed record of all coding changes you make, including the date, time, and specific parameters modified.
- Stay Updated: Stay updated on the latest DTS Monaco features, coding procedures, and vehicle information.
- Seek Training: Consider enrolling in advanced training programs to enhance your car coding skills and knowledge.
By following these best practices, you can minimize the risks associated with car coding and ensure that your modifications are safe, effective, and compliant with all applicable regulations.
Manufacturer sub-codes within DTCs offer a wealth of additional information, and DTS Monaco stands ready to display them when available, leading to quicker, more accurate diagnoses. Expand your skillset with DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN, where comprehensive training awaits to transform you into a car coding expert. Ready to take your diagnostic capabilities to the next level?
Address: 275 N Harrison St, Chandler, AZ 85225, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN. Contact us now to explore our courses and unlock the full potential of DTS Monaco!
FAQ Section
1. What is DTS Monaco used for?
DTS Monaco is a diagnostic and car coding software used for Mercedes-Benz vehicles, allowing technicians to perform advanced diagnostics, ECU programming, and car coding functions. It’s used to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), flash ECUs, and customize vehicle settings.
2. Is DTS Monaco difficult to learn?
DTS Monaco can be complex, especially for beginners. However, with proper training and practice, it can be mastered. DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers comprehensive courses designed to guide users from basic operations to advanced car coding techniques.
3. What is a J2534 Pass-Thru device?
A J2534 Pass-Thru device is an interface that connects your computer to a vehicle’s OBD-II port, enabling communication with the vehicle’s control units (ECUs). It’s required to use DTS Monaco for diagnostics, ECU flashing, and car coding.
4. Can I use DTS Monaco on any car?
DTS Monaco is primarily designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. While it might work on other brands, compatibility and functionality may vary.
5. What are CBF and SMR-D files?
CBF (Common Base Format) files contain communication protocols and diagnostic routines for specific ECUs, while SMR-D (Software Module Record – Data) files contain the actual data used for coding and configuration. Both are essential for DTS Monaco to function correctly.
6. How important is it to backup ECU data before coding?
Backing up ECU data before coding is extremely important. It allows you to restore the original settings if something goes wrong during the coding process, preventing potential damage or malfunctions.
7. What are the risks of car coding?
Risks of car coding include software corruption, voiding the vehicle’s warranty, compromising safety systems, and violating legal compliance. Proper training and following best practices can minimize these risks.
8. Do I need a seed key calculator for car coding?
Yes, a seed key calculator is often needed for car coding, especially when modifying protected control units. It provides the necessary security access to unlock the ECU before coding can be performed.
9. How can I stay updated on the latest DTS Monaco features?
Stay updated by following DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN, attending industry conferences, joining online forums, subscribing to newsletters, and participating in training programs.
10. Where can I get training on DTS Monaco?
DTS-MONACO.EDU.VN offers extensive resources and training programs designed to equip you with the skills needed to effectively use DTS Monaco for advanced diagnostics and car coding.
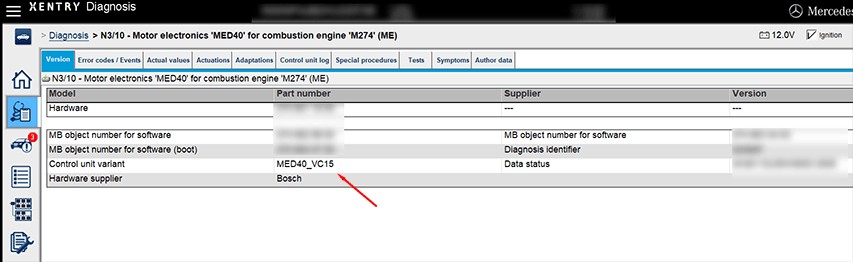 DTS Monaco Diagnostic Interface
DTS Monaco Diagnostic Interface
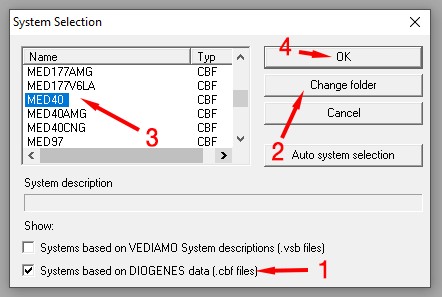 Vediamo ECU Selection
Vediamo ECU Selection
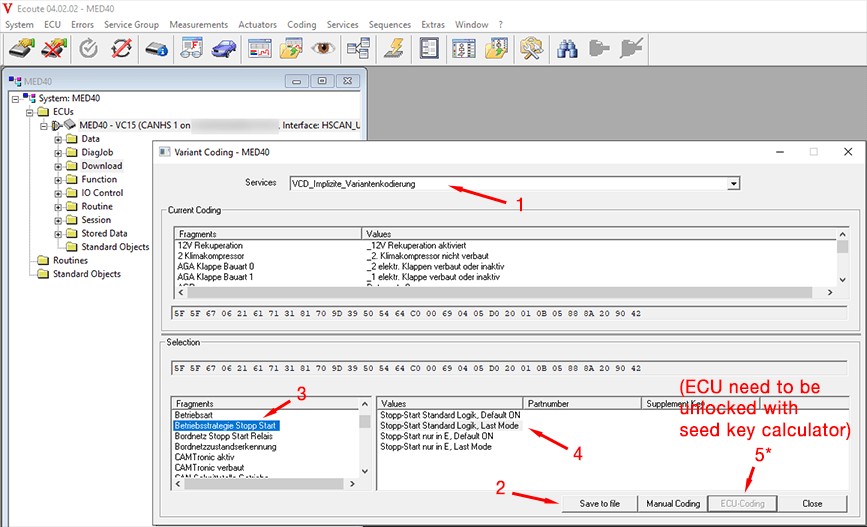 MED40 Coding Screen
MED40 Coding Screen
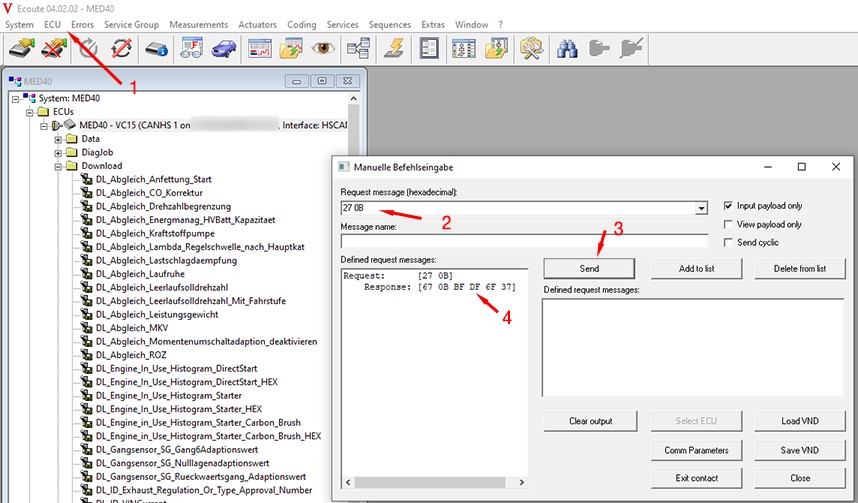 Manual Command Input in Vediamo
Manual Command Input in Vediamo
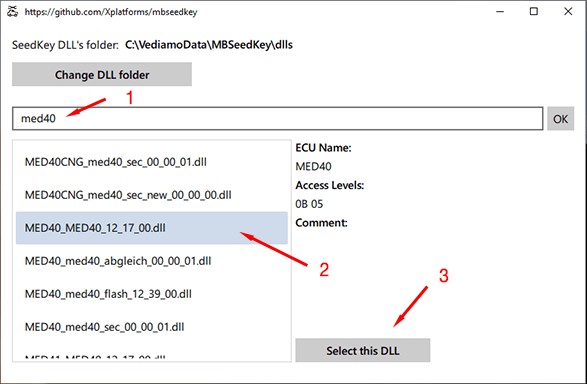 MBSeedKey Calculator Interface
MBSeedKey Calculator Interface
 Selecting DLL in MBSeedKey
Selecting DLL in MBSeedKey